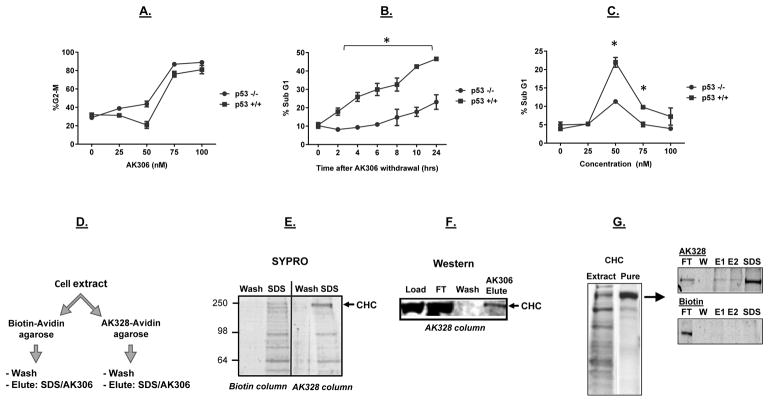
Figure 2.
The impact of p53 on AK306-induced G2/M arrest and apoptosis. A) A similar dose-dependent G2/M arrest in p53 wild type and mutant HCT116 cells. G2/M arrest was determined by flow cytometry. B) HCT116 cells were arrested with AK306, and then released from arrest by compound withdrawal (media change). The p53 wild type cells showed higher levels of apoptosis between 2 and 24 hours, as quantified by cell fragmentation. C) A spike in p53-promoted apoptosis was observed a 50 nM AK306. At higher concentrations, cells arrested in G2/M. Asterisks indicate a significant increase in apoptosis in p53-wild type treated cells (p < 0.01). D) Schematic of affinity chromatography experiments to identify cellular targets. HCT116 cell extracts were passed over an avidin column bound with AK328-biotin or biotin (a negative control). Bound proteins were then eluted with SDS or AK306. E) Columns were run as described in 2D. Shown are the final wash and the SDS elution from a biotin and an AK328-biotin column analyzed by SDS PAGE and SYPRO staining. The 200 kDa band enriched in the AK328-biotin eluate was excised and identified as CHC by LC-MS. F) HCT116 cell extract was loaded on the AK328-biotin column, and then eluted with 1 μM AK306. CHC was detected by western blotting in the load, flow through (FT), final wash and AK306 eluate. G) CHC purified from mouse liver extract was analyzed by SYPRO staining (left panel). Purified CHC was loaded on an AK328-biotin or biotin control columns, eluted with to sequential AK306 washes (1 μM, E1 and E2), followed by an SDS elution. The resulting fractions were analyzed by SDS PAGE followed by SYPRO staining (right panels).