Figure 1. Role of CBLB during viral infections.
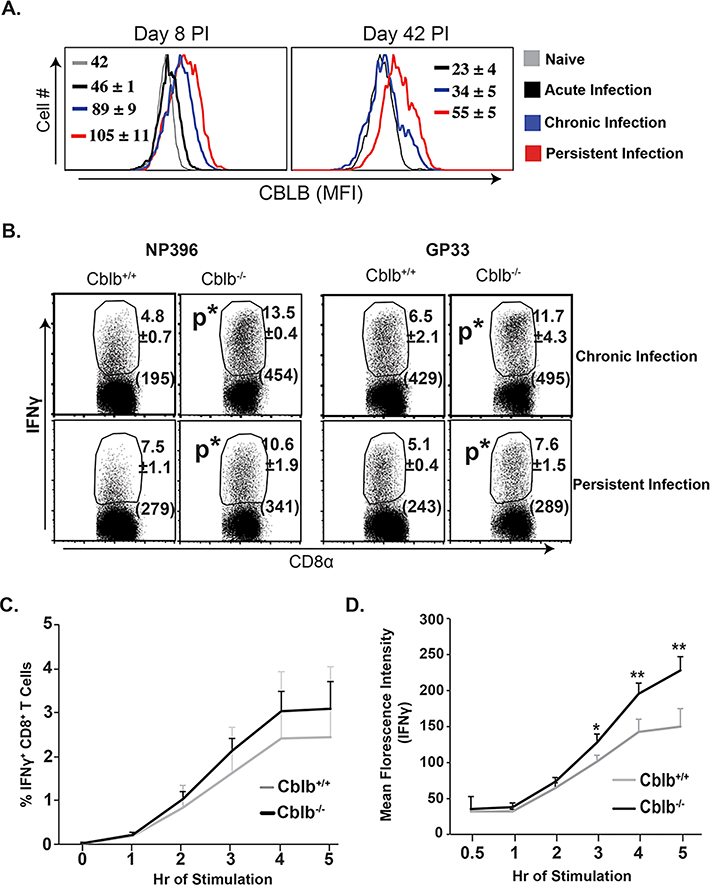
Naïve Cblb+/+ and Cblb−/− mice were inoculated with LCMV strains to produce acute (Arm), chronic (Clone 13) or persistent (Clone 13, CD4-depleted) infections. (A) Levels of CBLB expression. Values are Mean Florescence Intensity (MFI) ±SD. (B) LCMV-specific CD8+ T cell responses. Values are percent ± SD and MFI of IFNγ (parentheses). (C & D) Epitope-specific CD8+ T cell responses following recombinant DNA (LCMV-NP) vaccination. Percent (C) and IFNγ expression in MFI (D) of CD8+ T cell responses. N=4–5mice/group. *p≤0.05.
