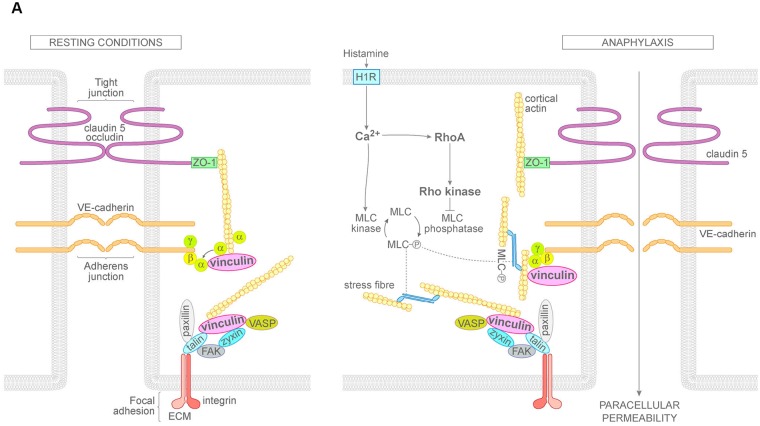
Figure 8.
Mechanisms of histamine-induced endothelial barrier disruption. Under resting conditions, vinculin is localized mainly along endothelial cell borders and at least in part co-localizes with VE-cadherin and α-catenin at AJs. In anaphylaxis, histamine induces a rapid increase of cytoplasmic Ca2+ leading to activation of RhoA. Both events induce stress fiber formation at focal adhesions. In addition, RhoA via Rho kinase may enhance tension on α-catenin at endothelial AJs which causes AJ reorganization. H1R = Histamine receptor type I; Ca2+ = calcium; MLC = myosin light chain; FAK = focal adhesion kinase; VASP = vasodilator-stimulated phosphoprotein; ZO-1 = zonula occludens protein1; α, β, γ = α-, β-, γ-catenin; ECM = extracellular matrix.