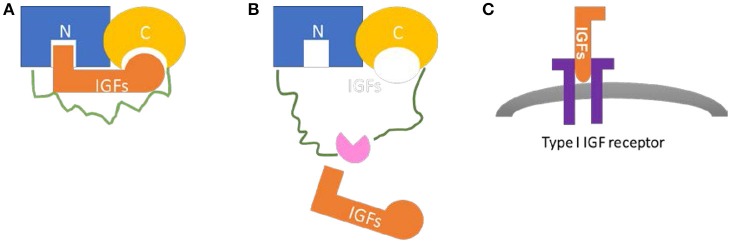
Figure 1.
Common structure and biological function of IGFBPs. (A) The N-terminal region (blue) and the C-terminal region (yellow) are connected by a linker region (green). Both N-domain and C-domain contains a binding site for IGFs (orange). (B) The proteolysis of IGFBPs by various proteases (pink) occurs in the linker region or other post-translational modifications, may result in IGFs release. (C) Once released from IGFBPs, IGFs bind to IGF receptors (purple) to exert their physiological effects.