Figure 2.
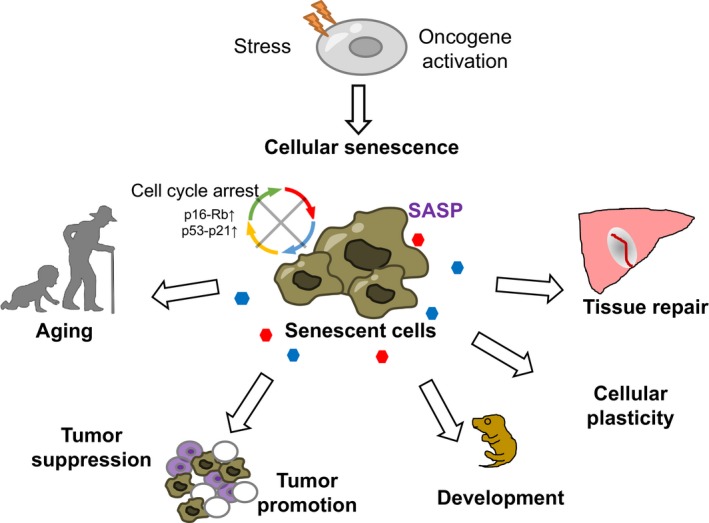
Diverse roles of cellular senescence in pathophysiological conditions. Cellular senescence is a state of a stable cell cycle arrest regulated by the p53‐p21 and p16‐Rb pathway, and can be induced by a range of cellular stresses. Senescent cells have functions not only in aging but also in various pathophysiological conditions, such as normal development, tissue repair, and cancer prevention, as well as cancer promotion through both cell autonomous and noncell autonomous mechanisms. Senescent cells exert diverse effects on the neighboring cells and the tissue microenvironment although the senescence‐associated secretory phenotype (SASP)
