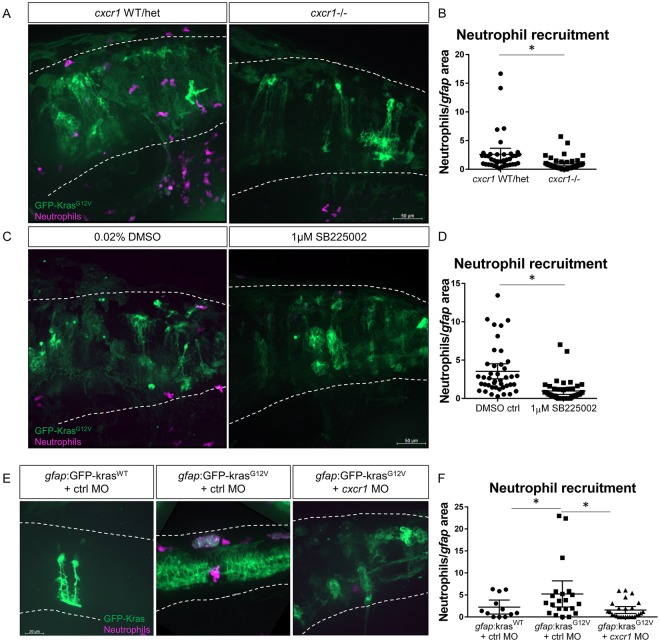
Figure 4.
Cxcr1 promotes neutrophil recruitment to the tumor-initiating microenvironment. Adult cxcr1 heterozygote zebrafish expressing Tg(mpx:mCherry) were in-crossed, injected with gfap:krasG12V, imaged for neutrophil recruitment to the hindbrain at 3 dpf, and then processed for single-embryo genotyping (A). Neutrophils recruited to the field of view were quantified in cxcr1 mutants and WT or heterozygote siblings (no difference observed between +/+ and +/−) and normalized to total gfap-expressing area (B, n = 40 WT/het and 44 cxcr1 mutant larvae). Tg(mpx:mCherry) larvae expressing gfap:krasWT or krasG12V were treated beginning at 2.5 dpf with 1 µM SB225002 or 0.02% DMSO vehicle control for 16 hours followed by live-imaging (C). Neutrophil recruitment was quantified and normalized as above (D, n = 42 DMSO and 43 SB225002 larvae). Wildtype Tg(mpx:mCherry) embryos were co-injected with gfap:GFP-krasWT or krasG12V and standard control MO or cxcr1 splice-blocking morpholino. Larvae were live-imaged at 3 dpf (E) and neutrophil recruitment was analyzed as described previously (F, n = 12 krasWT, 21 krasG12V ctrl MO, and 26 krasG12V cxcr1 MO larvae). *p < 0.05, One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s test performed for data in 4 F.