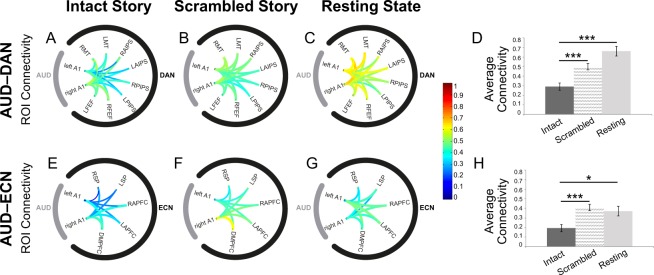
Figure 5.
Functional connectivity between the auditory and fronto-parietal networks in healthy wakeful individuals, during the audio story and baseline conditions. Connectivity between the auditory and fronto-parietal networks was significantly modulated by the presence of complex meaningful stimuli, with the functional differentiation between the AUD and DAN/ECN increasing significantly in the audio story as compared to the scrambled story and resting state baseline conditions. (A–C) Connectivity between the ROIs within the AUD and DAN networks in the intact story (A), scrambled story (B), and resting state (C) baseline. (D) Average AUD–DAN connectivity (z values) for each condition. (E–G) Connectivity between the ROIs within the AUD and ECN networks in the intact story (E), scrambled story (F), and resting state (G) baseline. (H) Average AUD–ECN connectivity (z values) for each condition. A1: Primary auditory cortex; LFEF: Left frontal eye field; RFEF: Right frontal eye field; LPIPS: Left posterior IPS; RPIPS: Right posterior IPS; LAIPS Left anterior IPS; RAIPS: Right anterior IPS LMT: Left middle temporal area; RMT: Right middle temporal area; DMPFC: Dorsal medial PFC; LAPFC: Left anterior prefrontal cortex; RAPFC: Right anterior prefrontal cortex LSP: Left superior parietal; RSP: Right superior parietal.