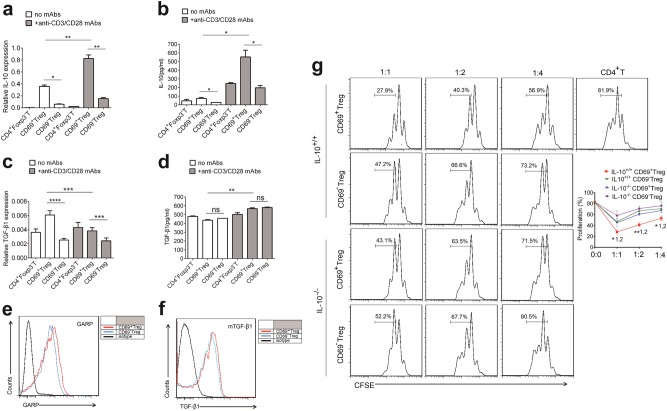
Fig. 2. CD69+ Tregs inhibit effector T cell proliferation in an IL-10-dependent fashion.
a, c Overall 1 × 106/ml freshly isolated Treg cell subsets or CD4+Foxp3−T cells from Foxp3GFP knock-in mice were stimulated with or without 2 μg/ml anti-CD3/CD28 antibody for 24 h and the relative levels of Il-10 and TGF-β1 to β- actin in the cells were analyzed by real-time PCR (n = 3). b, d The levels of IL-10 and TGF-β1 in the supernatants of cultured cells as described in a and c were measured by ELISA. e, f The expression levels of GARP and mTGF-β1 in CD69+ Treg and CD69−Tregs were analyzed using flow cytometry with indicated antibodies. g 1 × 106 /ml CD4+CD25−T cells were labeled with CFSE and co-cultured with CD4+CD25+CD69+ Tregs or CD4+CD25+CD69−Tregs from Il-10+/+ or Il-10−/− mice at a ratio of 1:1, 1:2, or 1:4 in the presence 1 μl anti-CD3/CD28 coated beads for three days. Then, the proliferation of CD4+ T cells was analyzed using flow cytometry. The cells were gated first on living lymphocytes and then CFSE+ T cells (n = 3). Date are representative images or expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, and Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns, no significant. 1, versus CD69− Tregs from Il-10+/+ mice; 2, versus CD69+ Tregs from Il-10−/− mice