Fig. 6.
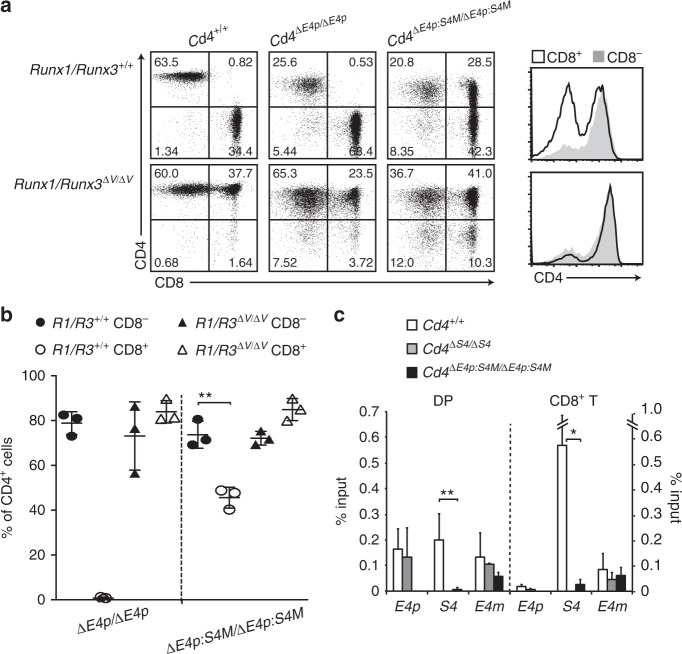
Involvement of Runx in regulating the helper-lineage dominant activity of E4m. a Dot plots showing CD4 and CD8 expression in lymph node T cells of mice with indicated genotypes. In Runx1/Runx3ΔV/ΔV mice, both Runx1 and Runx3 proteins lack the VWRPY motif, which is essential for interaction with TLE/Groucho co-repressors. Right histograms showing CD4 expression level in CD8− and CD8+ lymph node T cells of Cd4ΔE4p:S4M/ΔE4p:S4M mice with (lower) or without (upper) Runx1/Runx3ΔV/ΔV mutation. Numbers in quadrants indicate respective cell percentages. One representative result of three independent analyses. b Summary of percentage of CD4+ cells in CD8− and CD8+ lymph node T cells of Cd4ΔE4p/ΔE4p, Cd4ΔE4p:S4M/ΔE4p:S4M mice with or without Runx1/Runx3ΔV/ΔV mutation. Means ± SD. **p < 0.01 (unpaired student t test, two-sided). c Graph showing summary of three independent ChIP-qPCR for Runx bindings to E4p, S4, and E4m regions in DP thymocytes (DP) and CD8+ T cells from Cd4+/+, Cd4ΔS4/ΔS4 and Cd4ΔE4p:S4M/ΔE4p:S4M mice. Means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (One-way ANOVA and Tukey’s multiple comparison test)