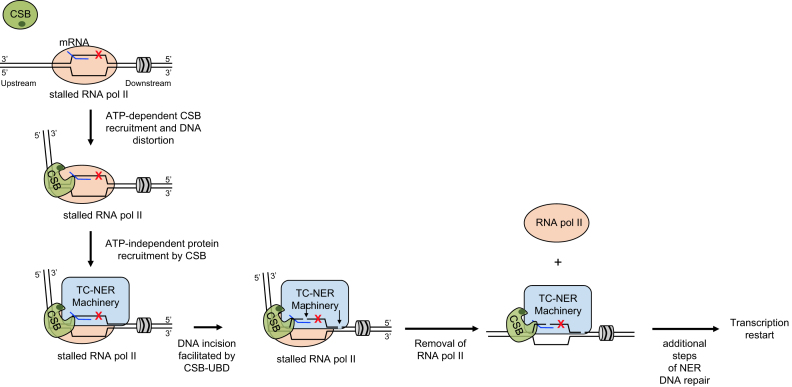
Figure 3.
Model for how CSB integrates into different steps of TC-NER. The association of CSB with RNA pol II stalled at a bulky DNA lesion (red X) is stabilized. This step requires the DNA/nucleosome stimulated ATP hydrolysis activity of CSB. CSB interacts with both RNA pol II and duplex DNA upstream of RNA pol II as well as single-stranded DNA within the upstream fork of the transcription bubble. CSB generates an 80-degree bend in the upstream DNA and provides an interaction surface for recruiting additional TC-NER factors. CSB facilitates this step through protein-protein interactions, but not through its ATP-dependent chromatin remodeling activity. The C-terminal Ub-binding domain (dark green oval) of CSB is needed for efficient DNA incision. Dual incisions (arrows) happen in the presence of RNA polymerase II, which is subsequently removed to permit the remaining steps of the repair processes.