Figure 1.
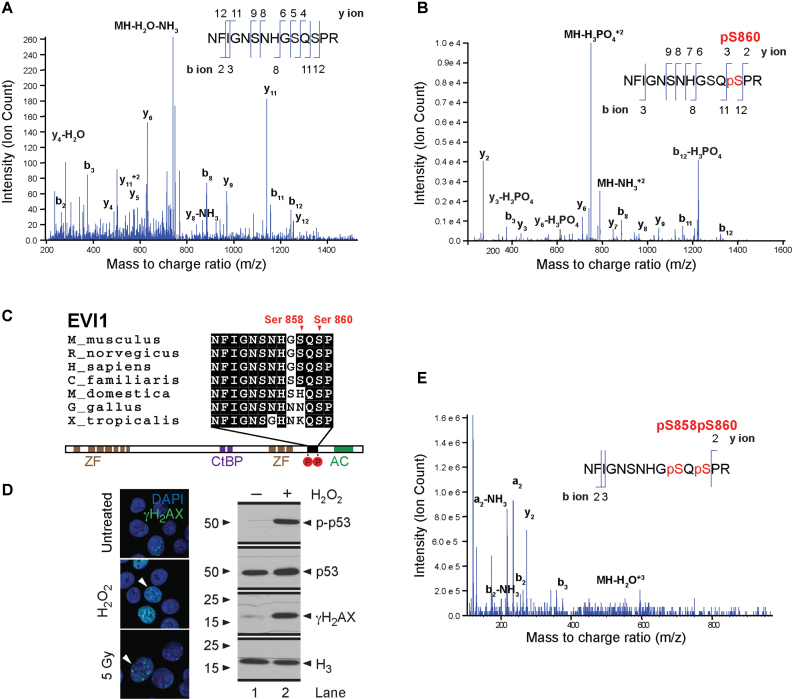
Carboxy-terminal EVI1 phosphorylation. Mass spectrometry analysis of the EVI1 peptide Asn849-Arg862 from SB1690CB AML cells, demonstrating the presence of non-phosphorylated (A) and single Ser860 phosphorylated peptides (B) in untreated SB1690CB cells. y- and b-type ions illustrating their position within the peptide sequence indicated. The mass/charge ratio (m/z) of the precursor ion is also shown. (C) Schematic representation of the EVI1 protein with sequence alignment of EVI1 from other species as indicated, showing DNA binding zinc finger domains (ZF), CtBP1 binding motifs (CtBP) and acidic domain (AC). Carboxy-terminal phosphorylation sites are shown in red circles and annotated in relation to the EVI1-SQS containing epitope alignment. (D) Confirmation of induction of DNA damage by γH2AX foci formation after H2O2 or radiation treatment of SB1690CB cells (left panel). White arrowheads denote cells with increased number of foci (green signal). DAPI co-stain for the nucleus (blue signal). Western blot (right panel) of γH2AX and p-p53 (Ser15) as markers of DNA damage response activation and ATM activity after H2O2-treatment of SB1690CB cells. (E) EVI1 MS spectrum obtained for peptide Asn849-Arg862 from irradiated SB1690CB cells, inferring double phosphorylation of the carboxy-terminal S858/S860 SQS motif.