Fig. 2.
O-Glycosylation found on Notch EGF repeats in mammalian cells.
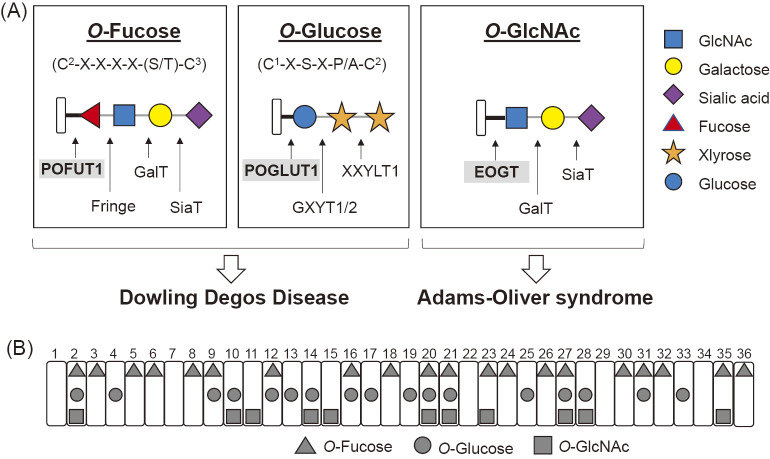
(A) The structures of O-linked glycans found in mammalian Notch receptors are illustrated with each consensus sequence. C1 and C2 are the first and second conserved cysteine residues of the individual EGF domains, respectively. C3-C6 are represented in a similar manner. The consensus sequence for O-GlcNAc modification has not been defined, but was predicted to be C5XX(G/P/S)(Y/F/W)(T/S). Mutations in POFUT1 or POGLUT1 cause Dowling–Degos disease, whereas mutations in EOGT cause Adams-Oliver syndrome. The solid black line indicates the basic linkage in the O-glycan, whereas the thin gray line indicates the linkage once extension occurs. (B) Glycosylation sites on EGF repeats in the extracellular domain of mouse Notch1 receptors expressed in HEK293T cells were determined by mass spectrometry59): O-Fucose (triangle), O-Glucose (circle), O-GlcNAc (square).