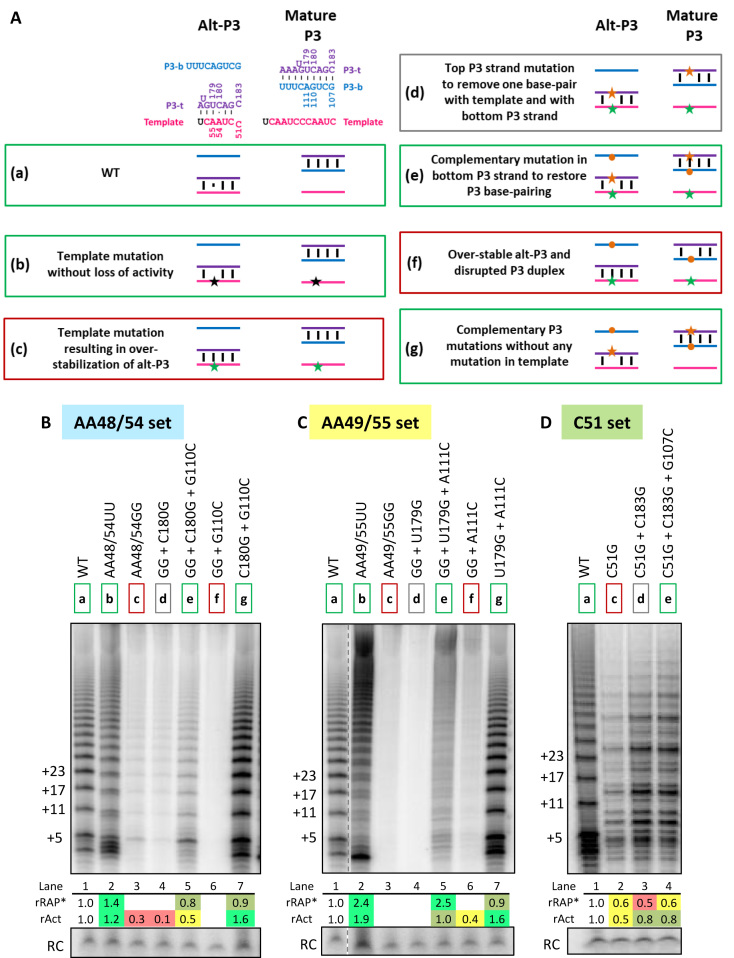
Figure 4.
Over-stabilization of alt-P3 inhibits the activity of telomerase assembled in vitro. (A) Compensatory mutation strategy to rescue template mutations with over-stabilized alt-P3. (a) Alt-P3 (left) and Mature P3 (right) states of WT hTRmin with the strand coloring used throughout the schematics. Numbering for the bases mutated in this assay is indicated. (b) Template mutation without loss of activity (black star). (c) Template mutation that would over-stabilize alt-P3 state (green star). (d) Top P3 strand mutation (orange star) to remove one base-pair with template and with bottom P3 strand. (e) Complementary mutation in bottom P3 strand (orange circle) to restore P3 duplex base-pairing. (f) Mutations in template and bottom P3 strand. (g) Mutations in top and bottom strands of P3 without any template mutation. Positive control and successful rescue combinations predicted to have high catalytic activity are boxed green, those with little to no activity are boxed in red, and others are boxed in gray. (B–D) Activity assays for rescue of mutation at different template positions: (B) AA48/54, (C) AA49/55 and (D) C51. Shading for these template mutation sets is same as in Figure 3. The hTRmin mutants were reconstituted in RRL and assayed with a template-specific primer in the presence of all dNTPs. Mutations are indicated with the corresponding color-coded boxed ‘a–g’ states. Values for rRAP* and rAct were calculated as described in Figure 3. Similar results were obtained from 2 independent experimental replicates.