Figure 3.
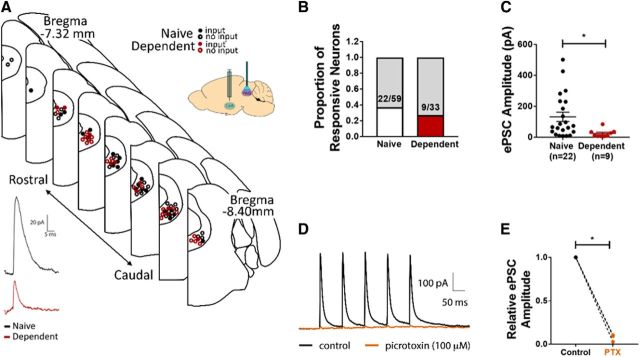
CeA inputs to vlPAG are weaker in alcohol-dependent rats. A, Top, Map indicating approximate positions of PAG neurons recorded from naive (black) and alcohol-dependent (red) rats. ChR2-containing CeA terminals were stimulated in PAG-containing brain slices (inset). Closed circles represent neurons in which an optically evoked postsynaptic current was observed. Open circles represent neurons in which optical stimulation evoked no events. Bottom, Sample recordings of optically evoked postsynaptic current of PAG neuron from naive (black) and alcohol-dependent (red) rats. B, No significant differences exist in the proportion of neurons in which evoked events were observed between groups. C, Average amplitude of evoked postsynaptic current was significantly lower in PAG neurons from alcohol-dependent rats compared with naive controls. *p < 0.05. D, Representative trace showing optically evoked current of PAG neuron in the absence (black) and presence (orange) of PTX. E, Superfusion of PTX significantly decreased the relative amplitude of evoked postsynaptic currents of PAG neurons. C, E, Data are mean ± SEM.