Figure 1.
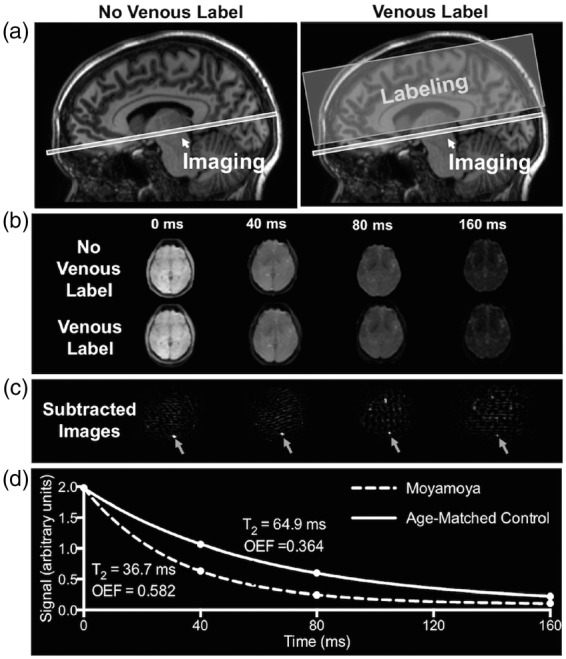
T2-relaxation-under-spin-tagging (TRUST) MRI for non-invasive quantification of whole-brain oxygen extraction fraction (OEF). TRUST-MRI is used to determine the Carr–Purcell–Meiboom–Gill (CPMG) T2 in the superior sagittal sinus, which has a known relationship with venous oxygenation (Yv). Arterial oxygenation (Ya) is measured by pulse oximetry. By taking the fractional difference in oxygenation (Ya-Yv)/Ya, OEF is calculated. A schematic of the venous blood imaging is shown in panel (a). Volume-selective venous labeling pulses are applied to invert inflowing venous blood water magnetization; these labeling acquisitions are interleaved with an image with no labeling (control image). Panel (b) shows representative control and label images at four different effective echo times (eTEs). Panel (c) shows the subtraction of the label image from control image, which allows for isolation of signal in the superior sagittal sinus. Signal intensities from the subtraction image (control-label) at the four eTEs are fitted to a known model (d) and venous blood water T2 is determined. Panel (d) shows T2 decay for a control with a normal OEF (T2 = 64.9 ms; Yv = 0.62; OEF = 0.364) and a participant with moyamoya (T2 = 36.7 ms; Yv = 0.41; OEF = 0.582).
