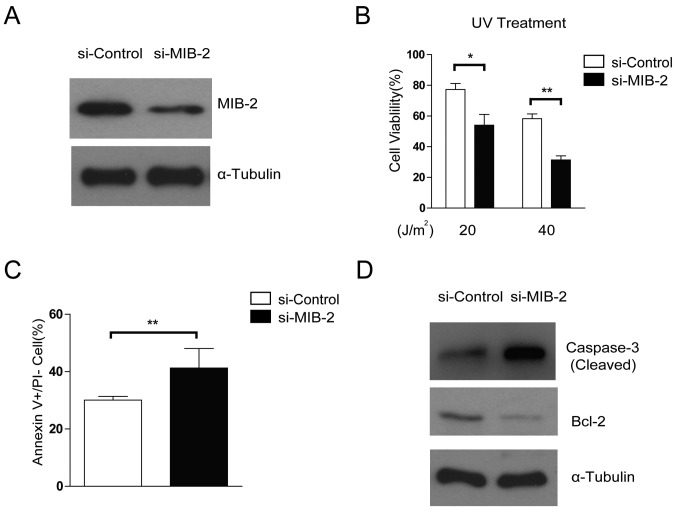
Figure 4.
Knockdown of endogenous MIB2 attenuates the resistance of glioma cells to apoptosis. (A) Knockdown of MIB2 in glioma cell lines was analyzed by WB. α-tubulin was used as the loading control. (B) Knockdown of MIB2 increases cell death. The indicated cells were treated by UV irradiation (20 and 40 J/m2) and counted for viable cells using the trypan blue exclusion assay. Data are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean of three experiments with statistical significance determined by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey's post hoc test. **P<0.01. (C) Knockdown of MIB2 enhances the sensitivity of glioma cells to UV-induced apoptosis. MIB2-knockdown glioma cell lines were treated with UV irradiation (40 J/m2), followed by Annexin V-fluorescein isothiocyanate and PI staining, and the number of Annexin V+/PI-cells was counted from 5 random fields. Results are expressed as percentages of total cells. Columns represent the mean of three experiments. A Student's t-test was used for statistical analysis. **P<0.01. (D) T98G cells were treated with UV irradiation (40 J/m2) and were harvested for cell lysate preparation. WB was performed to assess the levels of cleaved caspase-3 and Bcl-2 protein. α-Tubulin was used as the loading control. WB, western blotting; MIB2, E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase; PI, propidium iodide; UV, ultraviolet; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2.