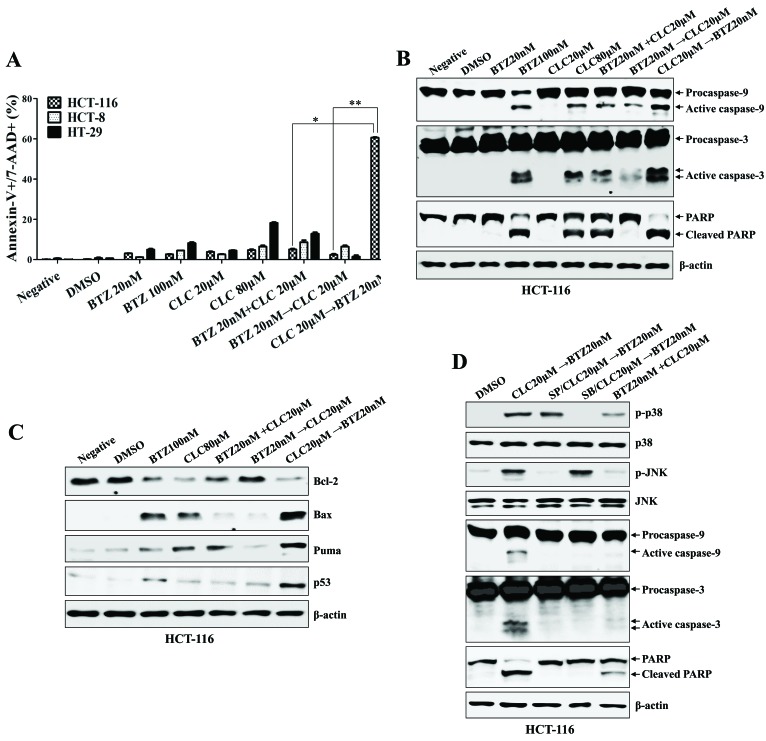
Figure 2.
Sequential treatment with CLC and BTZ enhances apoptotic death of colon cancer cells. HCT-116 cells were treated with BTZ or CLC individually or in combination. (A) Annexin-V/7-AAD staining was used to estimate the rate of apoptosis. The number of late-stage apoptotic cells (annexin-V+/7-AAD+) was calculated by flow cytometry. *P<0.01; **P<0.005. Cells from each indicated condition were harvested and blotted with the indicated antibodies, including (B) caspases (procaspase-9, active caspase-9, procaspase-3, active caspase-3 and PARP (full-length PARP, cleaved PARP), and (C) Bcl-2, Bax, PUMA and p53. β-actin served as an internal control. (D) To inhibit the activation of JNK or p38-mitogen-activated protein kinase, cells were pre-treated with SP600125 (20 µM) or SB203580 (10 µM) for 2 h. The expression of caspase-9, caspase-3 and cleaved PARP were detected by western blotting. The results are representative of three independent experiments. CLC, celecoxib; BTZ, bortezomib; 7-AAD, 7-aminoactinomycin D; PARP, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; negative, non-treated cell; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide control; p-, phosphorylated; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PUMA, p53-upregulated modulator of apoptosis.