Fig. 5.
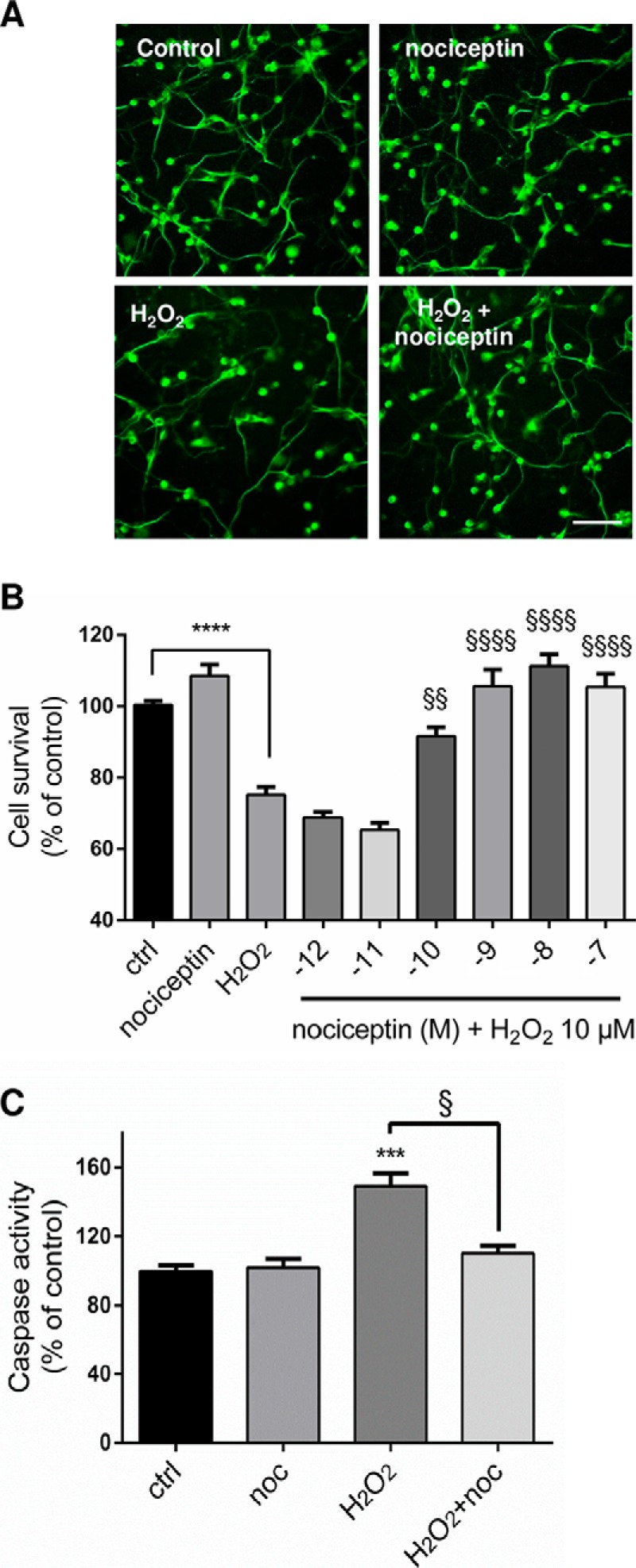
Nociceptin protects granule neurons from hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis. A, Typical images illustrating the protective effect of nociceptin against hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced cerebellar granule cell death. Scale bar = 65 μm. Cells were treated for 24 h with 10−5 m H2O2 and in the presence or absence of 10−8 m nociceptin and labeled with tubulin tracker green. B, Effect of graded concentrations of nociceptin (noc; 10−12 to 10−7 m) on survival of cultured cerebellar granule cells exposed to 10−5 m of H2O2 after 24 h of treatment. Cell survival was quantified by measuring fluorescein diacetate intensity. Results are expressed as percentages of control. Each value is the mean (± S.E.) of 4 wells from at least 10 independent cultures. For the nociceptin alone condition, cells were treated with 10−8 m nociceptin. Each value is the mean (± S.E.) of 4 wells from at least 8 independent cultures. Statistical analysis was performed with ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's test: ****p < 0.001 versus control; §§p < 0.01, §§§§p < 0.0001 versus H2O2. (C) Caspase activity of cells treated with 10−5 m H2O2 in the presence or absence of 10−8 m nociceptin. Statistical analysis was performed with the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by Dunn's test: ***p < 0.001 versus control, §p < 0.05 versus H2O2.
