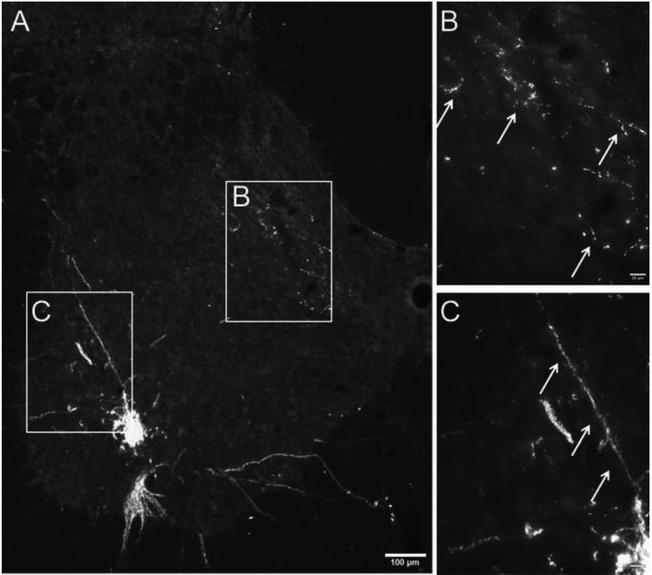
Figure 2. Phrenic afferent fiber vs. phrenic motoneuron dendrite labeling following CT-β application to the phrenic nerve.
Panel A shows a view of the left half of the C4 spinal cord; the areas highlighted by the boxes are shown at higher magnification in panels B and C. CT-β labelled afferent projections in the dorsal spinal cord were distinct in appearance from the CT-β labelled phrenic motoneuron dendritic projections. Phrenic afferent fibers were thinner with a relatively diffuse distribution of “punctate” synaptic terminals (B). In contrast, the phrenic motoneuron dendrites were more linear in appearance, and could be observed radiating from the cell soma (C). Another demarcating feature was the size of the dendritic boutons which were smaller compared to more bulbous synaptic boutons associated with the terminal endings of afferent fibers. Scale bars: 100μm (A) or 20μm (B-C).