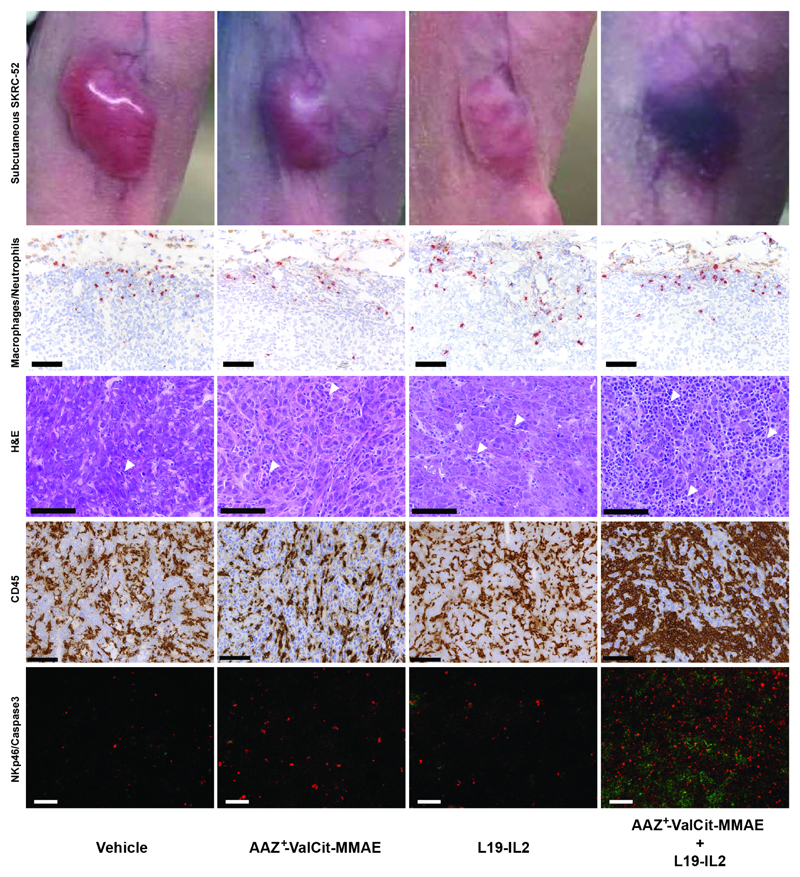
Figure 4. Ex vivo histological and immunofluorescence analysis on SKRC-52 tumor sections following treatment with vehicle, AAZ+-ValCit-MMAE (SMDC), L19-IL2 (immunocytokine) or the AAZ+-ValCit-MMAE/L19-IL2 combination.
Representative images of mice treated with saline, single agents or combination. H&E staining of tumor samples is depicted at a 30X magnification. Immunofluorescence analysis of tumor samples is depicted at a 10X magnification. Green = NKp46 staining; Red = Caspase 3 staining; Blue = DAPI staining. Immunohistochemistry analysis of tumor samples is depicted at a 20X magnification (scale bars: 100 μm). Red = myeloperoxidase-positive neutrophils; Brown = CD68-positive macrophages or CD45. Moderate numbers of neutrophils and macrophages infiltrate the periphery of all xenografts, without meaningful difference between the different therapy groups. A marked increase in infiltrating inflammatory cells (white arrowheads) is observed following treatment with the AAZ+-ValCit-MMAE/L19-IL2 combination. Increased numbers of infiltrating NK cells, associated with higher numbers of neoplastic apoptotic cells, are detected in the same group. All H&E pictures are taken from the center of the xenografts. The homogenous eosinophilic appearance observed in the nuclei of the neoplastic cells from the vehicle xenograft represents a freezing artifact.