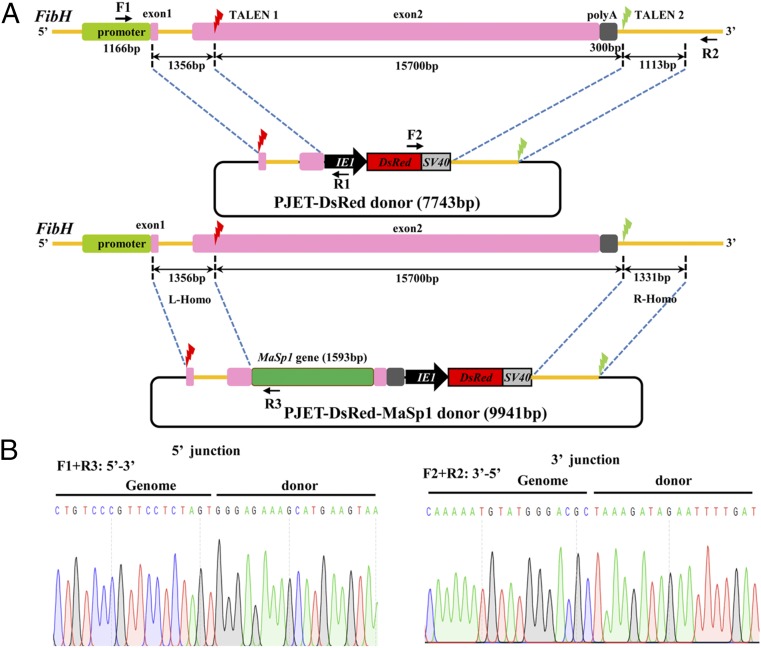
Fig. 1.
Schematic representation of the TALEN-mediated gene replacement system and the targeted integration of transgene constructs. (A) Schematic representation of the FibH gene and the TALEN targeting sites. The thin yellow line represents the FibH genomic locus, with the open boxes signifying the promoter, exons, and poly(A) signal. A 1,166-bp fragment (green box) located at the 5′ end represents the promoter region. The two 42-bp and 15,750-bp fragments (pink boxes) are exon 1 and exon 2, respectively. A 300-bp fragment (gray box) located at the 3′ end is the poly(A) signal. The red and green lightning icons indicate the two TALEN target sites. In the PJET-Red and PJET-MaSp1 donor constructs, a DsRed2 marker expression cassette driven by a baculovirus IE1 promoter was cloned into the PJET-1.2 vector. DNA fragments of 1,356 bp and 1,331 bp at the 5′ and 3′ ends flanking the TALEN sites were PCR-amplified, subcloned into vectors, and used as homologous arms (L-homo and R-homo, respectively). The 1,593-bp MaSp1 partial sequence is shown by the green box. Primer positions for amplification analyses of the integrated insertions in transformed silkworms are shown by arrows. Primer pairs of F1/R1 (or R3) and F2/R2 were used to amplify the 5′- and 3′-end insertion junctions, respectively. (B) Sequencing results of the integrated diagnostic DNA fragments to show 5′ and 3′ junction genome–donor integration.