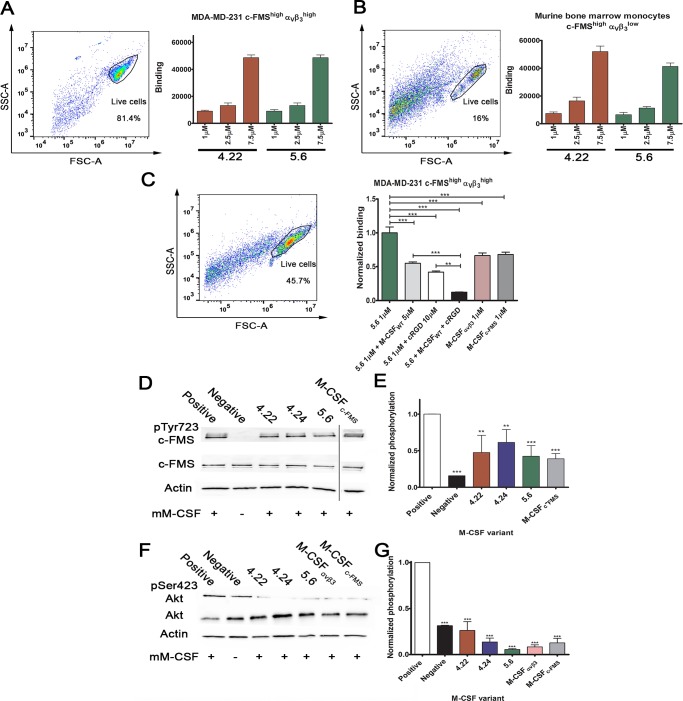
Fig 5. Cell binding, c-FMS, and Akt activation assays.
Purified M-CSFRGD variants 4.22 and 5.6 were tested for binding to (A) MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell line and (B) murine BMMs at different protein concentrations (1 μM, 2.5 μM, and 7.5 μM). The cellular expression levels of c-FMS and αvβ3 integrin are indicated as superscripts. (C) Cell competition binding assay for variant 5.6 in the presence and absence of the two competitors, namely 10 μM cRGD and 5 μM M-CSFWT. Binding of M-CSFc-FMS and M-CSFαvβ3 to the cells is shown for comparison. (D) Tyrosine phosphorylation of c-FMS and (F) serine phosphorylation of Akt in murine BMMs. Different gel runs are separated by a black line. (E) Relative c-FMS and (G) Akt phosphorylation levels of BMMs following incubation with M-CSFc-FMS, M-CSFαvβ3, and M-CSFRGD variants 4.22, 4.24, and 5.6 in the presence of recombinant M-CSF as a competitor. Chemiluminescence read-outs were quantified by densitometry. Data are means ± SEM of triplicates. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. The aspect ratios of the membranes in panels D and F were changed. Source data and analysis can be found in S2 Data. BMM, bone-marrow–derived monocyte; cRGD, cyclic RGD; M-CSF, macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MDA-MB-231, MD Anderson metastatic breast 231; RGD, Arginine-Glycine-Aspartic acid.