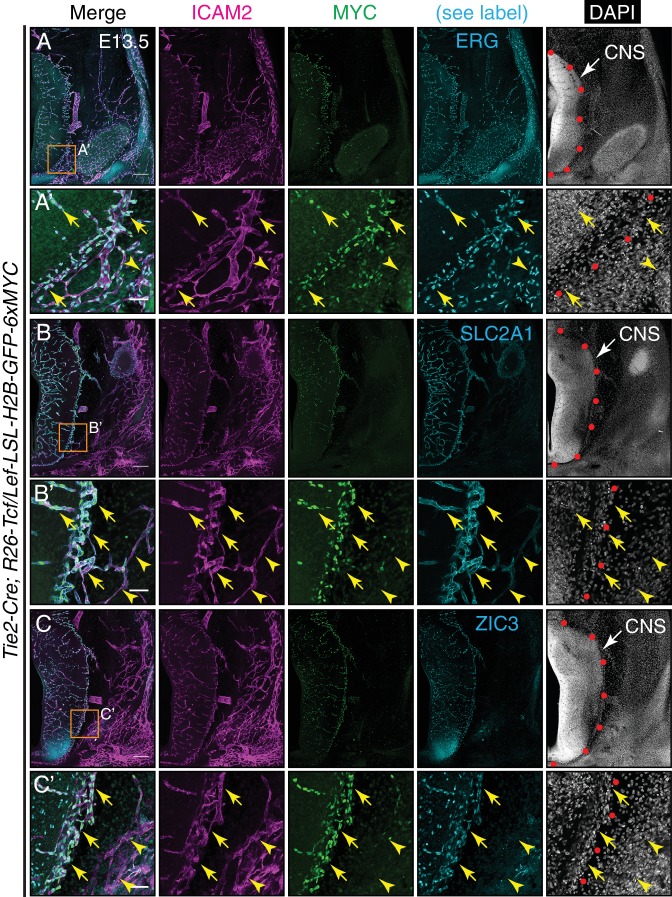
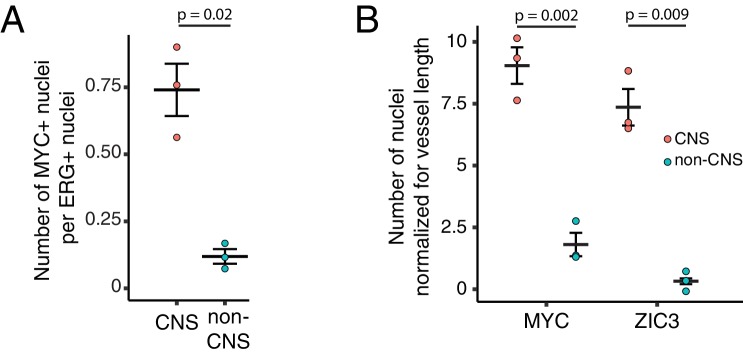
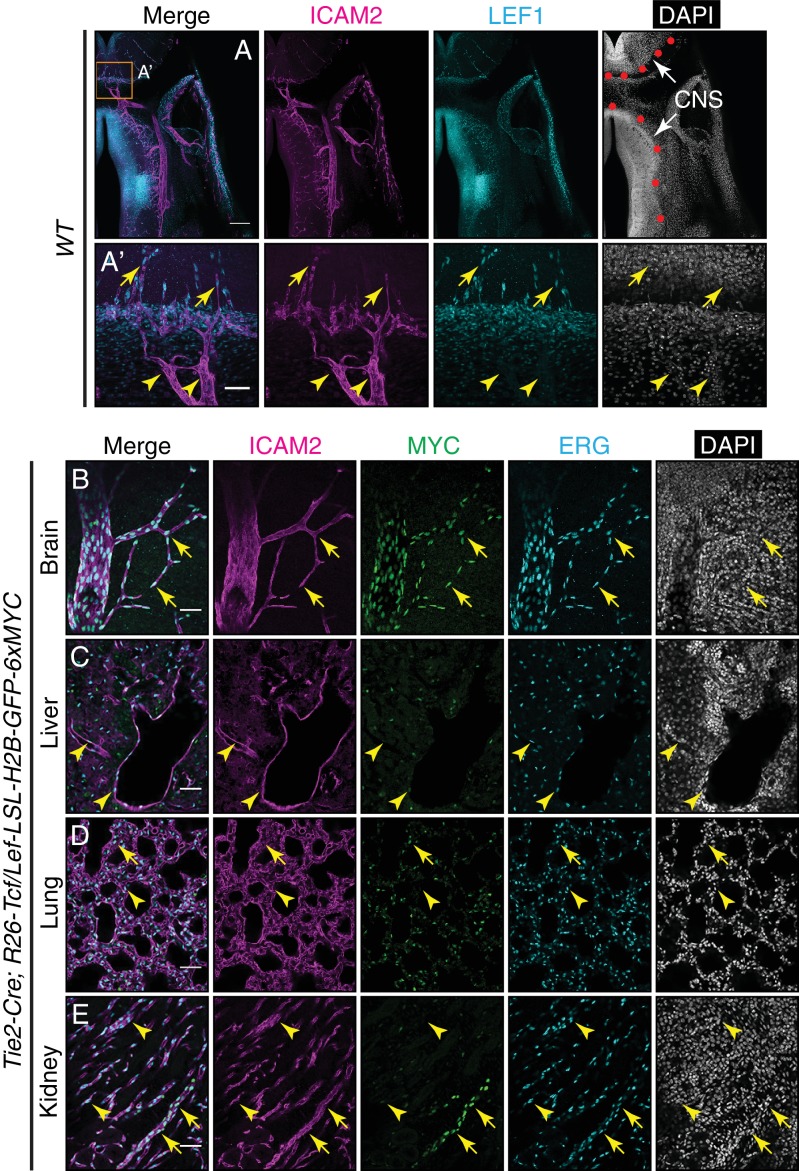
Figure 6. Canonical Wnt signaling in CNS but not peripheral ECs at E13.5.
(A–C) Coronal sections of E13.5 Tie2-Cre;R26-Tcf/Lef-LSL-H2B-GFP-6xMYC embryos near the cephalic flexure. The markers are: ICAM2 (pan-EC membrane protein), MYC (the canonical Wnt reporter), ERG (pan-EC TF), SLC2A1 (the glucose transporter GLUT1; a BBB marker), ZIC3, and DAPI. (A’–C’) Higher magnification of the boxed regions in (A–C). The boundary between CNS and peripheral tissue is marked on the DAPI image with red circles. The nuclear MYC signal reveals canonical Wnt signaling in CNS ECs (yellow arrows) but not in peripheral ECs (yellow arrowheads). ZIC3 is present in CNS ECs (yellow arrows) but not in peripheral ECs (yellow arrowheads), and in developing neurons in the ventral CNS. Scale bars in A, B, and C: 200 um. Scale bars in A’, B’, and C’: 50 um.