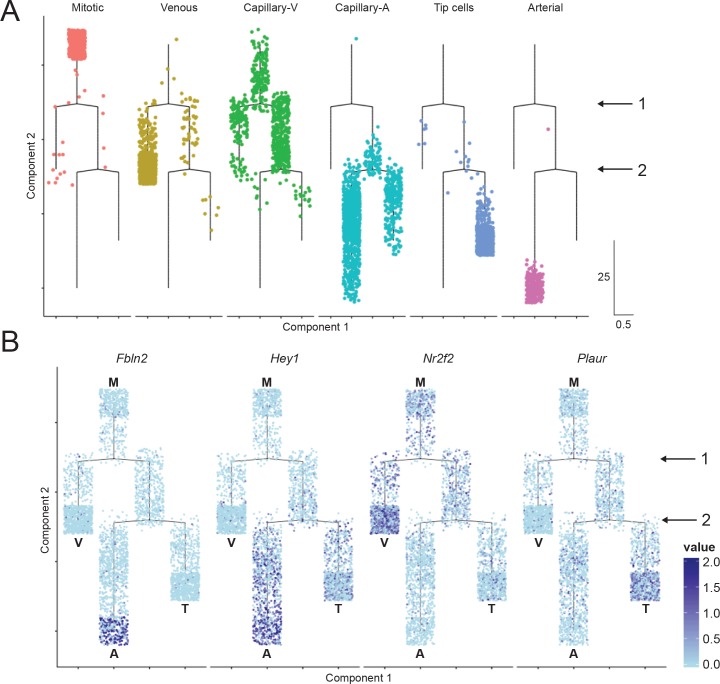
Figure 9. Cell trajectory analysis of brain ECs based on single-cell RNA-seq.
(A) Plot showing the position of cells in each EC cluster on the constructed cell trajectory. (B) Summary of the two branch points (labeled ‘1’ and ‘2’) in the cell trajectory analysis. M, mitotic; V, venous; A, arterial; T, tip cells. Examples of markers that show differential expression as cells diverge from branch points 1 and 2. Cells with no RNA-seq reads are shown in light blue; dark blue represents greater number of reads. Hey1 is enriched in arterial and tip cells (i.e. the products of the right side of branchpoint 1); Nr2f2 is enriched in venous ECs; Fbln2 is enriched in arterial ECs; and Plaur is enriched in tip cells.