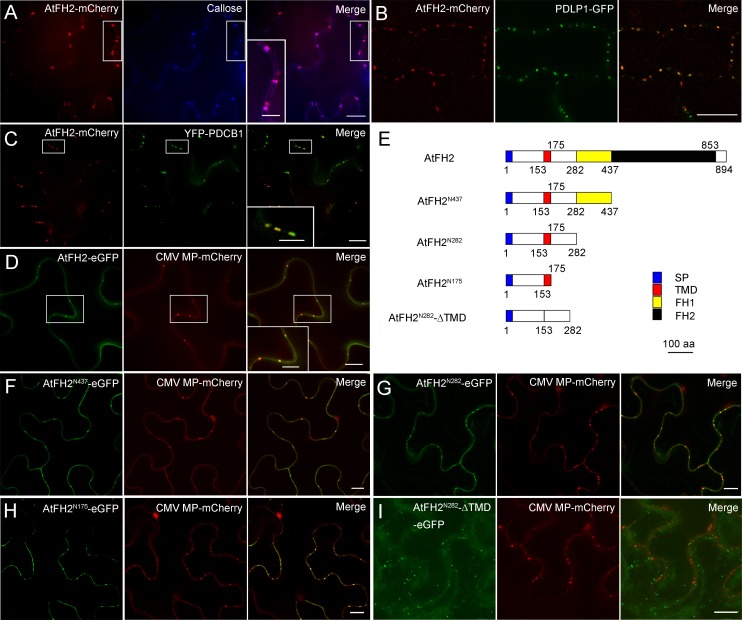
Figure 1. AtFH2 localizes to plasmodesmata and its PD localization is determined by the TM-containing N-terminus.
(A) Images of AtFH2-mCherry and callose (stained with aniline blue) in Arabidopsis epidermal pavement cells and the merged image. (B) Images of AtFH2-mCherry and PDLP1-eGFP in Arabidopsis epidermal pavement cells and the merged image. (C) Images of AtFH2-mCherry and YFP-PDCB1 in Arabidopsis epidermal pavement cells and the merged image. (D) AtFH2-eGFP, CMV MP-mCherry and the merged image in N. benthamiana leaf epidermal cells. (E) Schematic representation of AtFH2 and the truncated proteins used for the intracellular localization analysis. SP, signal peptide; TMD, trans-membrane domain. (F) AtFH2N437-eGFP, CMV MP-mCherry and the merged image in epidermal cells of N. benthamiana leaves. (G) AtFH2N282-eGFP, CMV MP-mCherry and the merged image in epidermal cells of N. benthamiana leaves. (H) AtFH2N175-eGFP, CMV MP-mCherry and the merged image in epidermal cells of N. benthamiana leaves. (I) AtFH2N282-ΔTMD-eGFP, CMV MP-mCherry and the merged image in epidermal cells of N. benthamiana leaves. Bars = 10 μm in all images, and bars = 5 μm in all inset images.