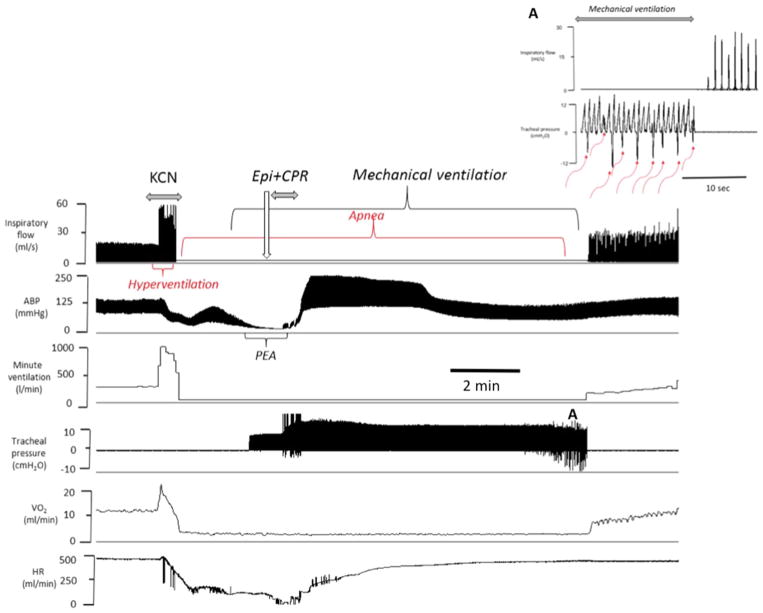
Fig. 7.
Example of the effects of epinephrine following KCN infusion (0.75 mg/kg/min) induced PEA in one spontaneously breathing rat. From top to bottom, inspiratory flow, arterial blood pressure, minute ventilation, tracheal pressure, O2 and heart rate are displayed. Following a brief period of hyperventilation, an apnea occurred followed by a rapid decrease in blood pressure, O2 and heart rate leading to a PEA. Epinephrine was administered while mechanical ventilation was initiated, as shown on the tracheal pressure signal. Circulation was restored within 30 s after the injection of epinephrine. Note that spontaneous breathing movements started to be generated within 10 min (red arrows) (Color figure online)