Figure 2.
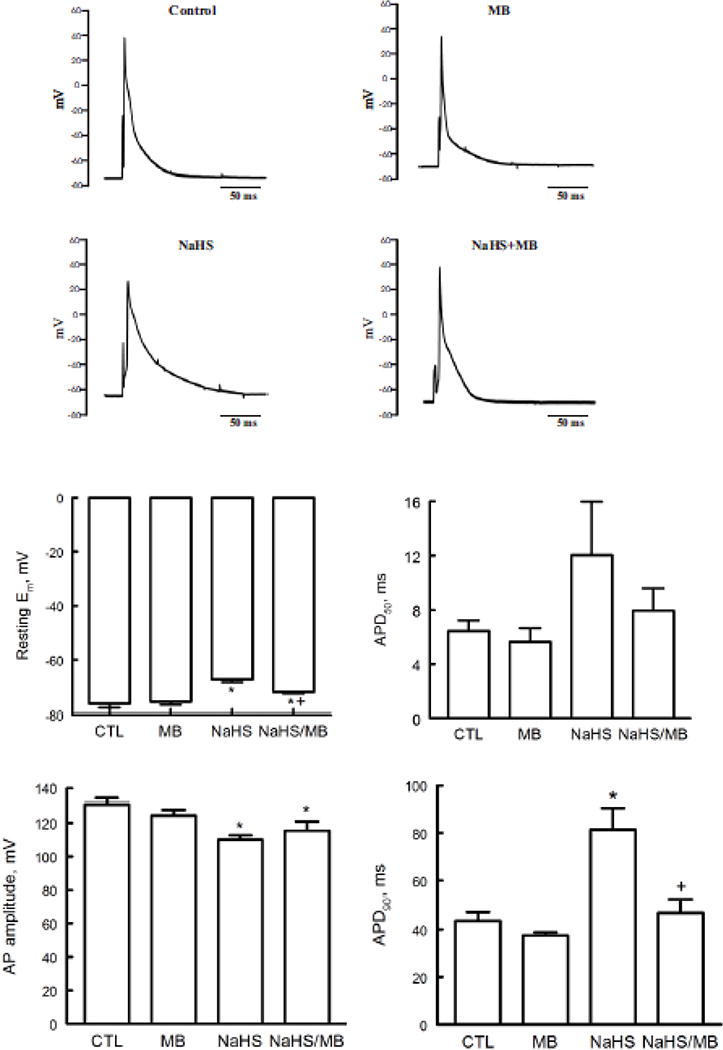
H2S depolarizes resting membrane potential (Em) and prolongs action potential duration (APD): rescue by MB. Em and APD were measured in myocytes isolated from mouse LV and septum with whole cell patch-clamp. Myocytes were paced at 1 Hz. Pipette solution consisted of (in mM) 125 KCl, 4 MgCl2, 0.06 CaCl2, 10 HEPES, 5 K+-EGTA, 3 Na2ATP, and 5 Na2-creatine phosphate (pH 7.2). External solution consisted of (in mM) 132 NaCl, 5.4 KCl, 1.8 CaCl2, 1.8 MgCl2, 0.6 NaH2PO4, 7.5 HEPES, 7.5 Na+-HEPES, and 5 glucose, pH 7.4. At time 0, either saline or NaHS (100 μM) was added followed by MB (20 μg/ml) or saline at 3 min before action potential was measured at 7 min. Top. Representative action potentials from myocytes treated with saline (control), MB alone, NaHS alone, and NaHS + MB recorded using current-clamp configuration at 1.5x threshold stimulus, 4-ms duration and at 30°C (75, 79, 96, 97). Bottom: Means ± SE of resting Em, action potential amplitude, action potential duration at 50% (APD50) and at 90% repolarization (APD90) from 5 control, 4 MB, 5 NaHS and 4 NaHS + MB myocytes are shown. * P<0.045, control vs. NaHS or NaHS + MB; + P<0.02, NaHS vs. NaHS + MB.
