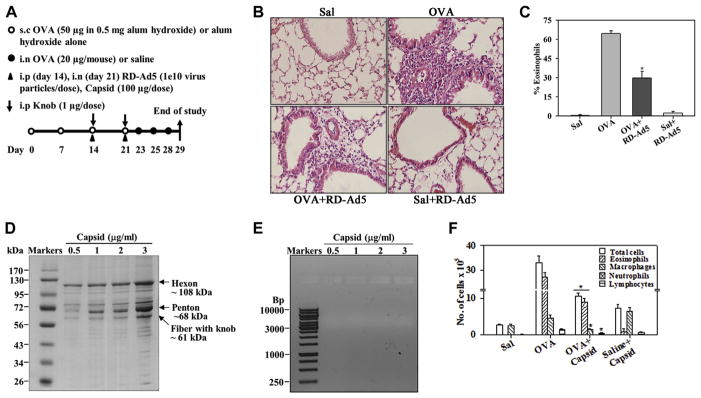
FIG. 1.
Inhibition of allergen-induced eosinophilia by RD-Ad5 and adenoviral capsid. A, Outline of mouse allergen (OVA) challenge model with details of RD-Ad5, capsid, and knob administration. s.c., Subcutaneous; i.n., intranasal; i.p., intraperitoneal. B, Representative data of cellular infiltration of lung tissue from saline- and OVA-challenged mice with and without RD-Ad5. Scale bar = 50 μm. C, Eosinophils in BALF of mice described in Fig 1, B. D, Representative Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE of capsid. E, Representative ethidium bromide–stained agarose gel of the capsid. F, BALF cell counts in saline- and OVA-challenged mice with and without capsid protein (n = 4 mice per group). Sal, Saline. *P < .001 in Fig 1, C, and P < .05 in Fig 1, F, compared with the OVA group.