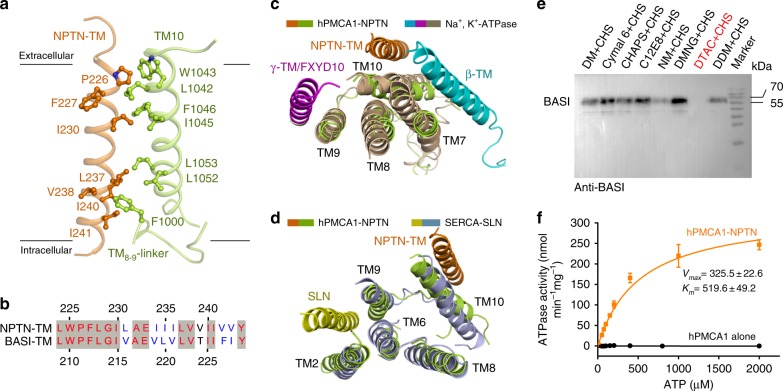
Fig. 2.
Interactions between the transmembrane regions of hPMCA1 and NPTN subunit. a NPTN-TM interacts with TM10 and the TM8-9-linker of hPMCA1. The hydrophobic residues on the interface are shown. b Sequence alignment of NPTN-TM and BASI-TM. c Structural comparison of the NPTN-TM binding site on hPMCA1 with that of β-TM and γ-TM/FXYD10 on Na+, K+-ATPase (PDB: 4HQJ). The α-subunit of Na+, K+- ATPase is shown in light brown, the β-TM is shown in cyan, and the γ-TM/FXYD10 is shown in magenta. The structure is viewed from the extracellular side. d Structural comparison of the NPTN-TM binding site on hPMCA1 with that of the SLN on SERCA (PDB: 4H1W). SERCA is shown in light blue, and the SLN is shown in yellow. The structure is viewed from the extracellular side. e Detergent screening for obtaining the hPMCA1 alone proteins. The complexes of hPMCA1-subunits fell apart by washing with DTAC-containing buffer. DM n-decyl-alpha-d-maltopyranoside, DMNG decyl maltose neopentyl glycol, NM n-nonyl-beta-d-maltopyranoside, DDM n-dodecyl-beta-d-maltopyranoside, C12E8 octaethylene glycol monododecyl ether, DTAC dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride, Cymal 6 6-cyclohexyl-1-hecyl-beta-d-Maltoside. f Measurement of ATPase activities of the hPMCA1-NPTN and hPMCA1 alone proteins. Each data point is the average of three independent experiments and error bars represent SD