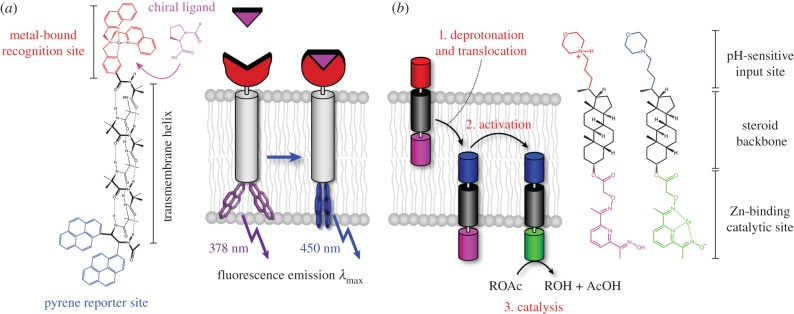
Figure 4.
De novo transmembrane components for signalling. (a) A synthetic GPCR mimic [136]. The synthetic receptor consists of a ligand-binding pocket featuring a cationic metal complex (red), an Aib oligomer (grey) and a pair of pyrene molecules attached to a chiral diamine (purple and blue). This complex adopts one of two mirror image conformational states on complexation with a chiral ligand. The binding of a chiral ligand (magenta) to one end of an Aib oligomer propagates its conformational influence along the entire length. The signal is output by the conformationally responsive fluorophore (purple and blue). Thus, the binding of the cofactor perturbs the global conformation, which is reported by the fluorophore component. (b) A translocatable sensor [137] in which two head groups are coupled to a steroid spacer (grey). The external sensor is a protonated morpholine (red or blue), while the second head group is a neutral pyridineoxime ‘pro catalyst’ (magenta or green). When the head groups are polar (red or green), they prefer to sit in the aqueous phase; when non-polar (blue or magenta), they prefer to sit in the membrane. Binding of a zinc cofactor from within the vesicle pulls the pro-catalyst head group into the aqueous phase on the interior of the vesicle. This allows the hydrolysis of the substrate within the vesicle, generating the output signal.