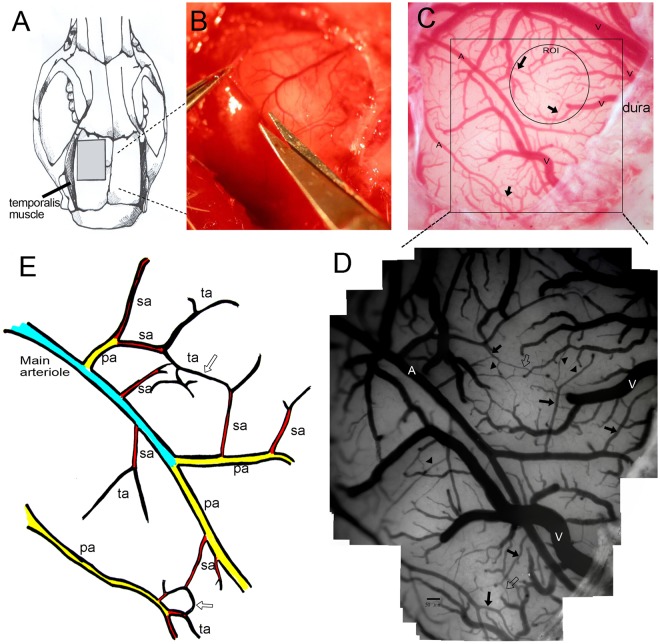
Figure 1.
The microcirculation system on the cortical surface of the rat brain. (A) A craniotomy of 5 × 5 mm2 was made behind the frontal suture. (B) The dura was opened using micro-scissors. (C) Under a dissection microscope equipped with a capillary videoscope at a resolution of 0.91 μm/pixel, all vasculatures on the brain surface, including the main arterioles and venules, were clearly seen (marked A and V to represent arterioles and venules, respectively). (D) This figure was created as a montage of 25 individual photos in order to obtain a panoramic view. In each craniotomy field, there were 1–2 main arterioles, which branched into primary arterioles (pa), secondary arterioles (sa), and terminal arterioles (ta). Terminal arterioles formed collateral circulation systems (hollow arrow) with each other, and finally disappeared from the brain surface. (E) Schematic diagram showing the microcirculation system on the brain surface.