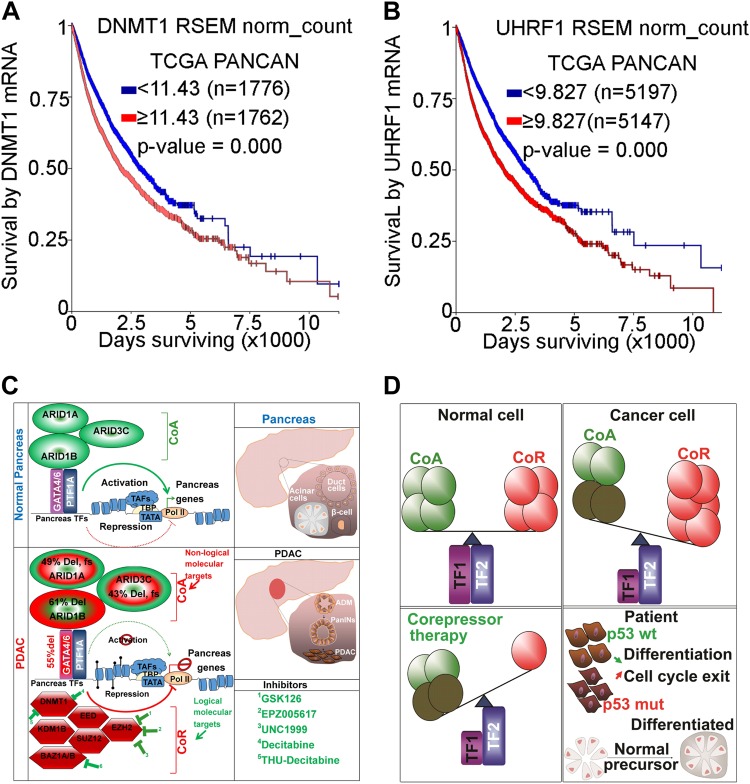
Fig. 5. Corepressor upregulation and model for inhibiting corepressors to re-engage forward-differentiation.
a Corepressor DNMT1 mRNA upregulation predicts poor survival across multiple human malignancies in TCGA PANCAN data. b Corepressor UHRF1 (that partners with DNMT1 for epigenetic repression activities) mRNA upregulation predicts poor survival across multiple human malignancies in TCGA PANCAN data. c Model example in PDAC alterations of coactivators and corepressors and candidate small molecules that can be used as corepressor therapy. d Model schematic summary for p-53 independent differentiation-restoring therapy. Non-malignant cells (normal cells) have intact lineage specifying transcription factors of cell fate determination that dynamically recruit coactivators and corepressors enzymes to turn on or turn off differentiation genes. Gene dose reduction by heterozygous deletion of a master transcription factor and inactivating mutations in its coactivators impairs the activation component of differentiation genes epigenetically6. Aberrant amplifications in transcriptional corepressor enzymes facilitate a closed chromatin status and epigenetically silence hundreds of differentiation genes6, 7 (Table 1). This mode of alteration is clinically relevant and can be developed to suppress proliferation even in TP53 mutant malignancies102, 105