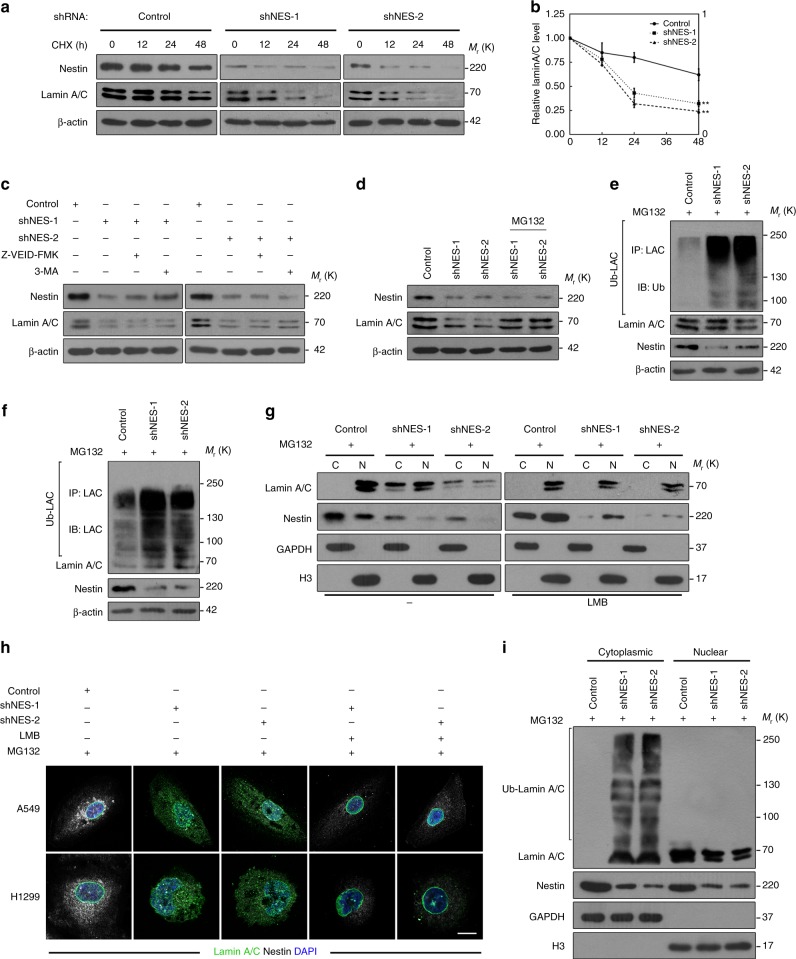
Fig. 5.
Nestin protects lamin A/C from proteasomal degradation. a, b Half-life analysis of lamin A/C in control and Nestin-knockdown A549 cells. All groups of A549 cells were treated with cycloheximide (50 μg/ml), harvested at the indicated times, and subjected to immunoblotting (a). Quantification of lamin A/C levels relative to β-actin is shown (b). c, d Identification of the pathway responsible for lamin A/C degradation upon Nestin knockdown. Control and Nestin-knockdown A549 cells were treated with Z-VEID-FMK (20 μM, 2 h), 3-MA (5 mM, 2 h) (c), or MG132 (20 μM, 6 h) (d), and then proteins were extracted and subjected to immunoblotting. e, f The effects of Nestin knockdown on ubiquitination of lamin A/C were analyzed by in vivo ubiquitination assays. Control and Nestin-knockdown A549 cells were treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h before harvest. Lamin A/C was immunoprecipitated with anti-lamin A/C antibody and immunoblotted with anti-Ub antibody (e) or anti-lamin A/C antibody (f). g, h Immunoblotting and immunostaining analysis of lamin A/C distribution in nucleus and cytoplasm. Control and Nestin-knockdown A549 cells were treated with MG132 (20 μM, 2 h) and then treated with or without 25 ng/ml LMB. After 4 h, the cells were fractionated for immunoblotting analysis (C cytoplasmic cell lysates, N nuclear cell lysates) (g) or stained with anti-lamin A/C antibody (green) and anti-Nestin antibody (white). Scale bars, 20 μm (h). i The effects of Nestin knockdown on ubiquitination of cytoplasmic lamin A/C were analyzed by in vivo ubiquitination assays. Control and Nestin-knockdown A549 cells were treated with MG132 (20 μM) for 6 h, harvested, and fractionated, and the cytoplasmic or nuclear lamin A/C fractions were immunoprecipitated and immunoblotted with anti-lamin A/C antibody. The quantified results were presented as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments, as assessed using two-way ANOVA test. **P < 0.01