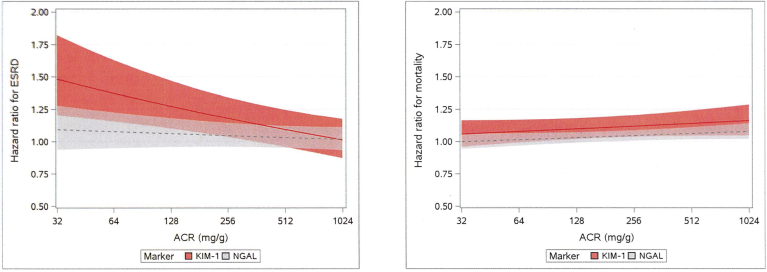
Figure 3.
Assessment of biomarker interactions for 10-year progression to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and all-cause mortality. Hazard ratios (HRs) (with 95% confidence intervals [CIs]) are shown per doubling of kidney injury molecule−1 (KIM-1) and neutrophil gelatinase−associated lipocalin (NGAL) across the range of albumin-to-creatinine ratios (ACRs). Estimates are from Fine−Gray (ESRD) or Cox (Death) models, controlling for demographics, socioeconomic status (SES), diabetes mellitus (DM), systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), hypertension (HTN), smoking, body mass index (BMI), alcohol use, ACR, C-reactive protein (CRP), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), urine creatinine, plus interaction terms for KIM-1−by-ACR or NGAL-by-ACR. Figure illustrates the interactions of urinary ACR with each biomarker for the outcomes ESRD and mortality. HRs are per doubling of urinary marker, using multivariable adjusted models controlling for demographics, SES, DM, SBP, DBP, HTN, smoking, BMI, alcohol use, ACR, CRP, eGFR, and urine creatinine.