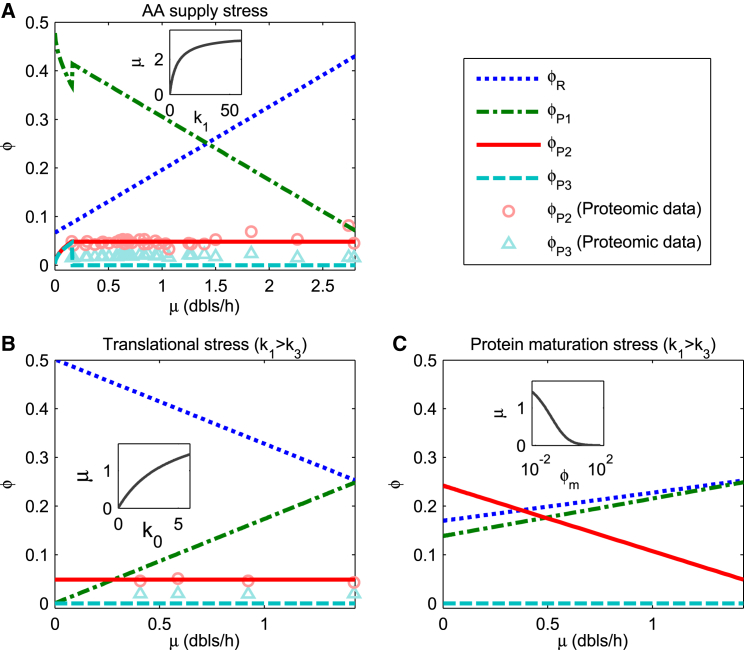
Figure 3.
The model predicts the relation of protein allocation fractions and the growth rate when one flux capacity (k1, k0, or 1/ϕm) is reduced by the stress. Insets present the decrease of growth rate with flux capacity limitation, in which units of μ, k1, k0, and ϕm are doublings/hour (dbls/h), h−1, h−1, and 1, respectively. ϕR, ϕP1, ϕP2, and ϕP3 indicate proteome fractions of ribosome-affiliated proteins (R class), AA-supply-required proteins (P1 class), chaperone-like proteins (P2 class), and protease-like proteins (P3 class), respectively. The experimental data for ϕP2 (circles) and ϕP3 (triangles) are obtained with the classification of Proteomaps (49); those in (A) are based on the proteomic data of (22, 28, 29, 30), and those in (B) are based on (22). Common parameters: ϕ∗ = 0.55, ϕ0 = 0.066, k3 = 0.3 h−1. (A) AA supply stress is shown by k1 decreasing. Parameters: k0 = 6 h−1 and ϕm = 0.0061. (B) Translational stress is displayed by k0 decreasing (k1 > k3). Parameters: k1 = 4.5 h−1 and ϕm = 0.0061. (C) Protein maturation stress is reflected by ϕm increasing (k1 > k3). Parameters: k0 = 6 h−1 and k1 = 4.5 h−1. To see this figure in color, go online.