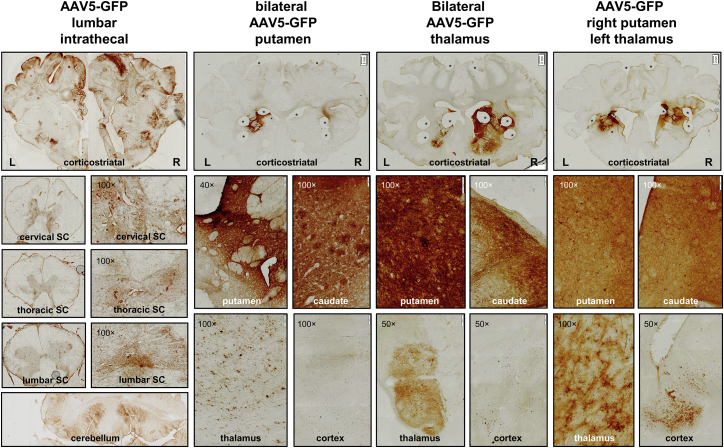
Figure 2.
AAV5-GFP Distribution after Intrathecal Injection of 5 × 1014 gc or Intracranial Injection into the Bilateral Putamen (1 × 1012 gc), Bilateral Thalamus (4 × 1012 gc), or Right Putamen and Left Thalamus Combined (2.5 × 1012 gc)
Top panels: GFP immunohistochemical staining of cortico-striatal brain slices. Upon intrathecal infusion, positive transduction was found in the cerebral cortex; cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spinal cord (SC); and cerebellum. Bilateral injection into the putamen resulted in strong putamen and caudate, and thalamic transduction, as well as GFP-positive neurons in the cortex. Bilateral injection in the thalamus caused thalamic transduction as well as GFP-positive neurons in striatal and cortical regions. Infusion into the right putamen and left thalamus showed a similar transduction pattern. Magnification factor is between ×1 and ×1.25. Asterisks indicate biopsies taken for biomolecular analyses. Scale bars, 2 mm.