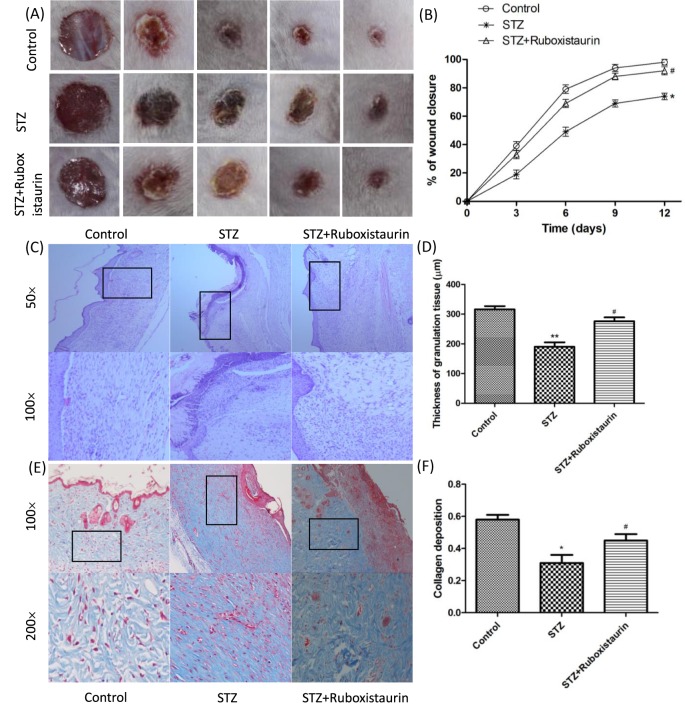
Figure 4. Ruboxistaurin accelerated wound healing in diabetic mice.
A 6.0-mm diameter wound was made by punch biopsy, and the closure of the wound area was measured every 2 days until day 12; ruboxistaurin accelerated the wound closure in STZ-induced diabetic mice (A,B). H&E staining of wound sections showed better dermal re-epithelialization as well as thicker granulation tissues in mice treated with ruboxistaurin compared with STZ group mice (C,D). Collagen deposition assessed by Masson’s trichrome staining showed more intense blue staining in ruboxistaurin-treated mice than in the STZ group, suggesting that ruboxistaurin treatment accelerated collagen deposition in the granulation tissues. Scale bar: 50.0 μm (E,F). **P<0.01, *P<0.05 compared with Control; #P<0.05 compared with STZ. The data are expressed as the means ± S.E.M. (n=10 per group).