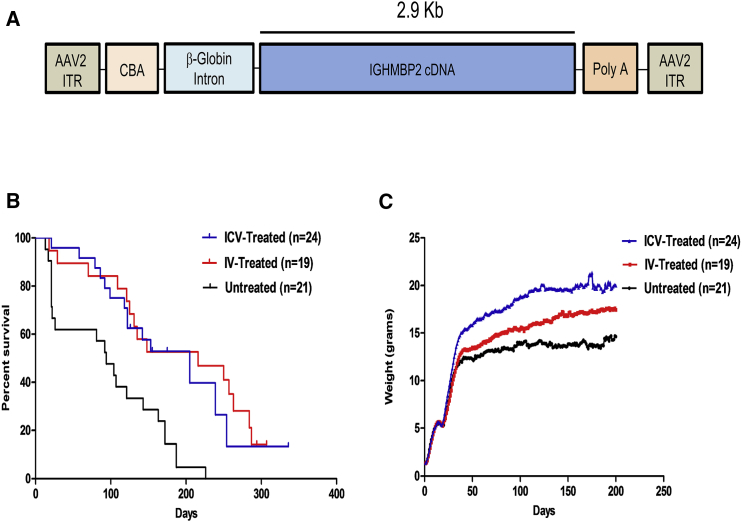
Figure 1.
ICV and IV Injection of AAV9-IGHMBP2 in Low Doses Significantly Increases the Survival and Total Body Weight of nmd Mice
(A) Map of AAV9-IGHMBP2 containing 2.9 kb of human IGHMBP2 cDNA under control of the ubiquitously expressing chicken-beta-actin (CBA) promoter along with an optimized intron within the 5′ leader sequence and a synthetic polyA site cloned into a single-stranded AAV vector. (B) Homozygous nmd mice were injected either ICV (at P2 and P3) or IV at P2 with a low dose (1.25 × 1011) of genomic copies of AAV9-IGHMBP2 and compared to untreated mice. Survival was determined by Kaplan-Meier curves, and the p value was determined by the log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. Median survival of ICV-injected nmd mice (n = 24) was 205 days and IV-injected (n = 19) 216 days compared to 94 days in untreated nmd mice (n = 21) (p = 0.0006). Median survival of IV- and ICV-injected nmd mice was not significant (p = 0.995). (C) Weight assessment of ICV- and IV-treated nmd mice compared to untreated mice. The average weight of ICV-treated nmd mice is 16.63 ± 0.33 g compared to 12.24 ± 0.21 g in untreated mice (one-way ANOVA p < 0.001) and 14.09 ± 0.28 g in IV-treated mice (one-way ANOVA p < 0.05). The average weight of IV-treated animals is significantly higher than untreated nmd animals (one-way ANOVA p < 0.01).