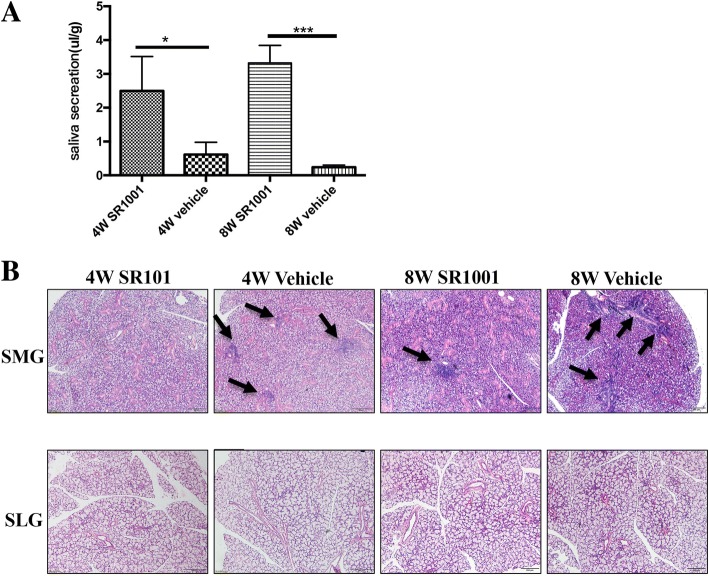
Fig. 5.
SR1001 improved salivary gland function and alleviated lymphocytic infiltration of salivary glands in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice. a SR1001-treated NOD mice exhibited normal salivary secretion, while significantly decreased saliva flow rate was observed in the both vehicle-treated 4-week-old (4W) and 8-week-old (8W) groups (n = 5 for each group); data represent means ± SEM (μl/g): *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. b Histological evaluation of glandular destruction in NOD mice was performed on tissue sections of submandibular glands (SMGs) (upper lane) and sublingual glands (SLGs) (lower lane) by H&E staining (n = 5 for each group). Arrowheads indicate inflammatory infiltrate foci. The upper micrographs showed fewer lymphocyte infiltration foci in SMGs of 4W SR1001-treated NOD mice at both 4 and 8 weeks of age compared to vehicle groups, and older NOD mice (8W) had mild inflammatory infiltration. The lower panel indicates no obvious sialadenitis in SLGs of NOD mice (n = 5 for each group). Scale bars = 100 μm