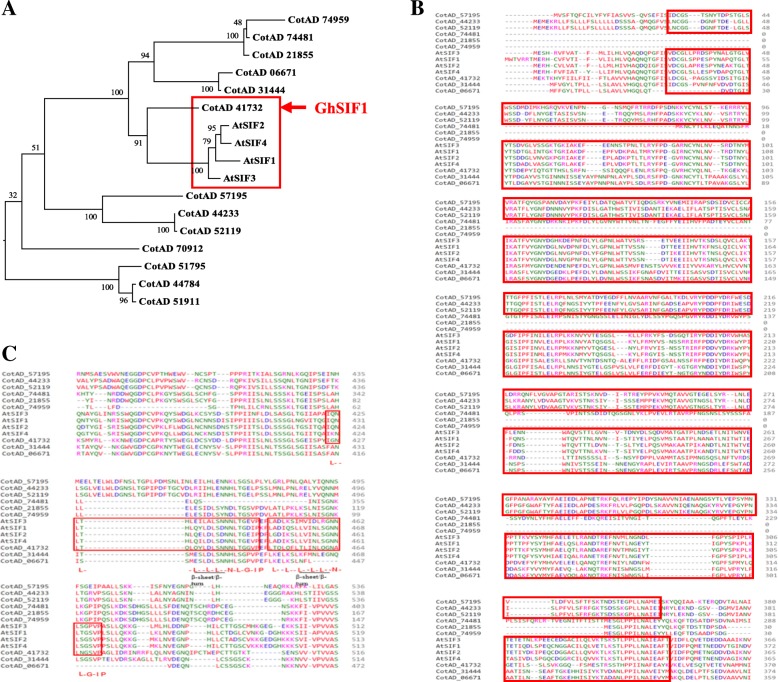
Fig. 2.
Phylogenetic tree of Arabidopsis thaliana SIF family and G. hirsutum LRR-RLK subclade I protein kinases. a The phylogenetic tree is constructed using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the JTT matrix-based model with MEGA 6. The analysis involved 13 G. hirsutum LRR-RLK subclade I protein sequences with 4 of Arabidopsis thaliana SIF family protein sequences. All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. b Alignment of Malectin-like domain and (c) LRR domain of AtSIFs and GhLRR-RLKs protein sequences. Protein alignment analysis was conducted with Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/). In the alignment, amino acid residues are depicted with different colors for distinguishing. Ellipses represent amino acid gaps. The numbers indicate the positions of amino acid residues. Malectin-like domain in (b) and LRR domains in (c) are highlighted with red boxes. In (c), ‘L--L--L--L-L--N-L--G-IP-’ indicates the conserved amino acid sequence of LRR domain, and the predicted β-strand/β-turn structure is underlined as --L-L--, where the ‘-’ stands for non-conserved amino acid residues, the ‘L’ represents Leu or Ile, and the ‘I’ represents Val or Ile