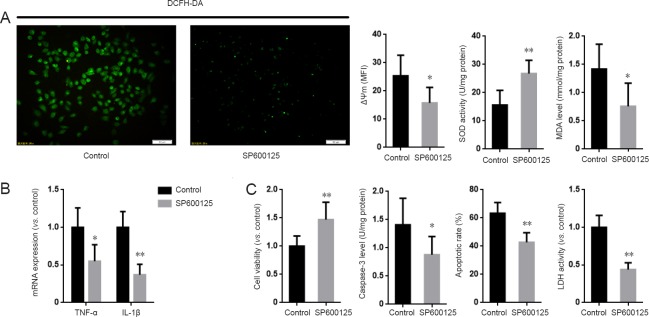
Figure 5.
Inhibition of JNK suppressed the aggravating effect of MKP1 knockdown on Aβ-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells.
(A) PC12 cells stably expressing MKP1 shRNA were treated without (Control) or with 2 μM of the JNK specific inhibitor SP6001250 in the presence of 10 μM Aβ42 for 24 hours. DCFH-DA fluorescence, mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), SOD activity and MDA levels were then analyzed. (B) Cells were treated as in A, and total RNA was extracted for quantitative real time-polymerase chain reaction for TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA with GAPDH as internal control. (C) Cells were treated as in A, and cell viability was assessed using the cell counting kit-8 assay, LDH activity and TUNEL staining. Data are representative images or are expressed as the mean ± SD (six separate experiments for each group). Intergroup comparison was performed using analysis of variance. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, vs. Control group. JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinase; MKP1: mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1; Aβ: amyloid beta; DCFH-DA: 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate; SOD: superoxide dismutase; MDA: malondialdehyde; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IL-1β: interleukin-1 beta; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; LDH: lactate dehydrogenase; TUNEL: terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling.