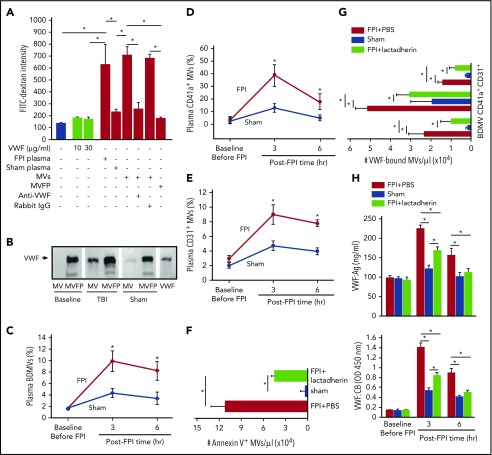
Figure 3.
The activity of VWF-bound MVs from different cells. (A) MV-induced increase in endothelial permeability is blocked by the VWF antibody (n = 16; 1-way ANOVA, *P < .01). (B) VWF is detected in the MV and MV-free (MVFP) fractions of plasma from TBI but only in MVFP fraction from sham mice. (C-E) The levels of plasma VWF+ MVs from brain cells (glial cells and neurons), platelets (CD41a+), and endothelial cells (CD31+) in the acute phase of TBI (n = 27; 1-way ANOVA, *P < .01 vs sham). Plasma levels of Annexin V+ (F) and VWF-bound MVs (G) in FPI mice treated with lactadherin or PBS and in sham mice (n = 12; 1-way ANOVA, *P < .001). (H) VWF:Ag (top) and VWF:CB (bottom) of plasma from C57BL/6J mice that received either 400 μg/kg of lactadherin or an equal volume of PBS before being subjected to FPI. Control mice underwent sham surgery (n = 12; 1-way ANOVA, *P < .01).