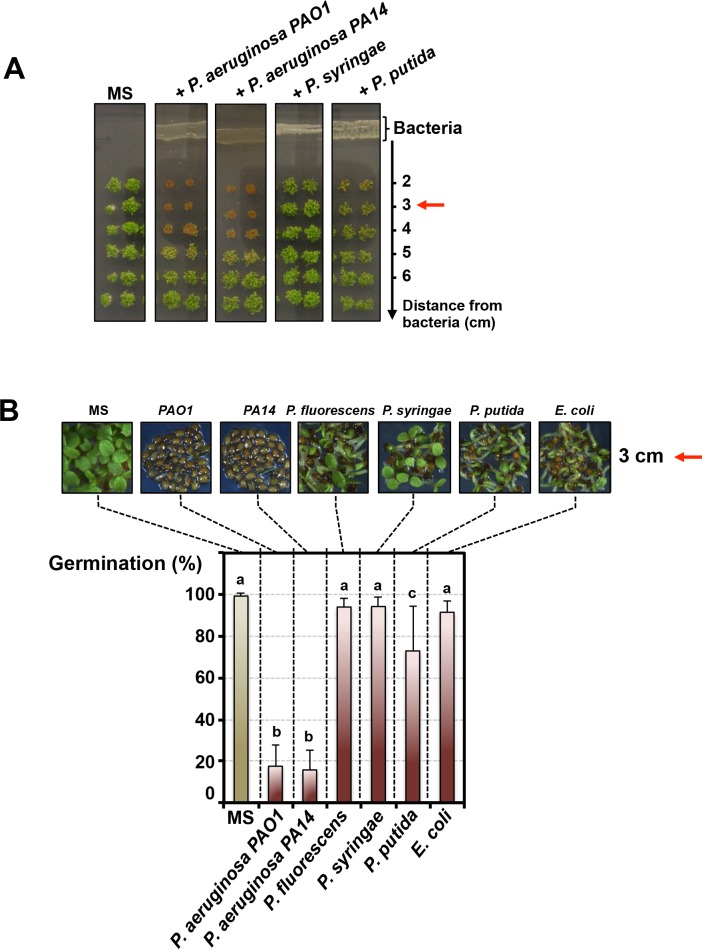
Figure 1. Pseudomonas aeruginosa releases a germination repressive activity (GRA).
(A) Pictures show Arabidopsis plants 4 days after sowing WT seeds in germination medium lacking bacteria (MS) or containing a given Pseudomonas species as indicated. Escherichia coli was included as a Gram-negative non-Pseudomonas species control. Note that seeds in close proximity of P. aeruginosa strains mostly did not germinate. Red arrows indicate distance used to calculate germination percentage in B. (B) Same experiment as in A. Representative pictures of plants 4 days after sowing seeds in germination medium in absence (MS) or presence of bacteria as indicated. Histograms show seed germination percentage 4 days upon sowing seeds in absence (MS) or presence of bacteria as indicated. Data represent mean ± standard deviation (nine replicates, n = 300–350). Lower case letters above histograms are used to establish whether two seed germination percentage values are statistically significantly different as assessed by one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey HSD test (p<0.05): different letters denote statistically different values.