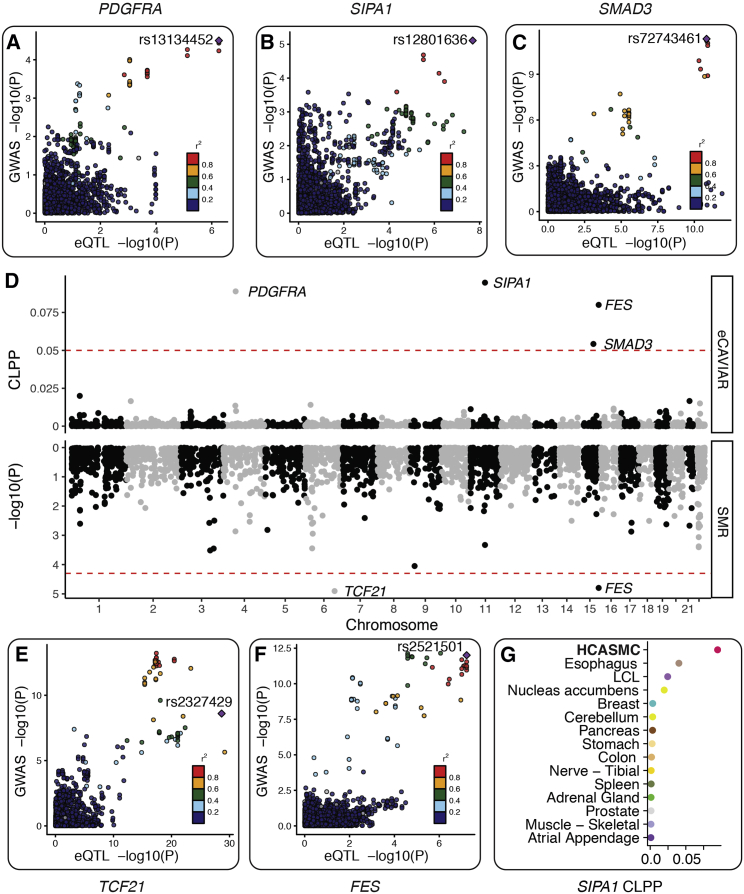
Figure 3.
Colocalization between HCASMC eQTL and Coronary Artery Disease GWASs
(A–C) Three candidate genes identified by eCAVIAR.
(A) Platelet-derived growth factor alpha (PDFGRA) eQTL signal colocalized with the KDR GWAS locus, which has p value < 3.16 × 10−5 (FDR < 0.05) in the latest CARDIoGRAMplusC4D and UK Biobank GWAS meta-analysis.6
(B) Signal-Induced Proliferation-Associated 1 (SIPA1) eQTL signal colocalized with the PCNX3 locus, which has p value < 7.75 × 10−6 in the UK Biobank meta-analysis, and reached genome-wide significance (p value < 9.71 × 10−9) in Howson et al.5 Note that the latter study has a larger sample size than the UK Biobank study.
(C) SMAD3 eQTL signal colocalized with the SMAD3 locus, which was identified in the UK Biobank meta-analysis.6
(D) Transcriptome-wide colocalization signals between HCASMC eQTL and CAD GWAS. We used eCAVIAR (top) and SMR (bottom) to fine-map GWAS causal variants and to identify eQTL signals that can explain CAD risk variants (see Material and Methods). We found five genes whose eQTL signals show significant colocalization with CAD GWAS signal (SMR FDR < 0.05 or eCAVIAR colocalization posterior probability > 0.05).
(E and F) Two candidate genes identified by SMR.
(E) Transcription factor 21 (TCF21) eQTL signal colocalized with the TCF21 locus, which was identified by Schunkert et al.74 and replicated in the UK Biobank meta-analysis.
(F) FES eQTL signal colocalized with the FURIN-FES locus, which was identified by Deloukas et al.75 and replicated in the UK Biobank meta-analysis.
(G) SIPA1 colocalization is strongest in HCASMCs, suggesting that this gene may influence CAD risk through this specialized cell type.