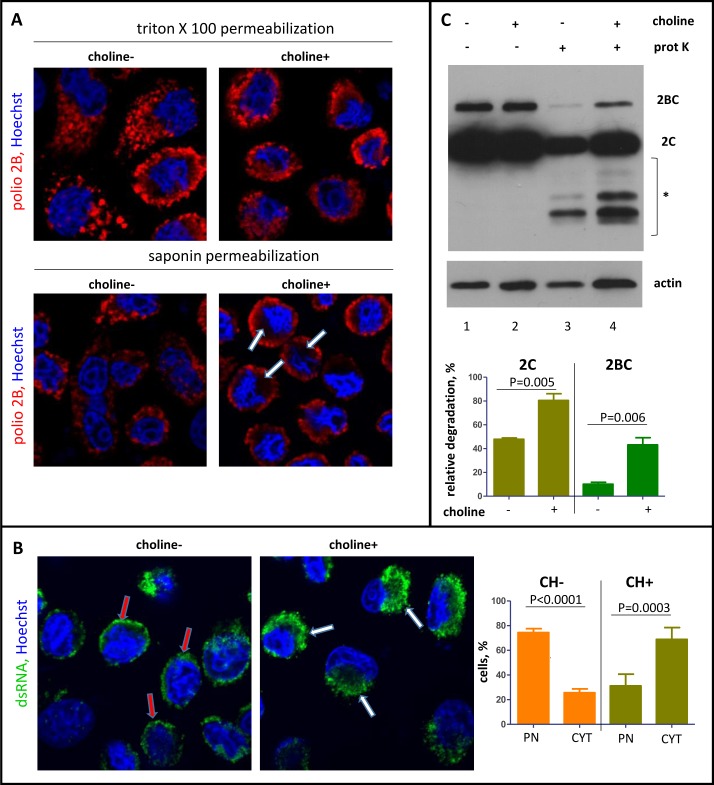
Fig 8. Inhibition of phospholipid synthesis affects the accessibility of the replication complexes.
HeLa cells after choline deprivation were infected with poliovirus at an MOI of 10 PFU/cell and incubated in a choline-free or a choline-supplemented medium after infection. A. Confocal images of the cells permeabilized with either 0.2% Triton X100 (strong permeabilization) or 0.02% saponin (mild permeabilization) and stained for a viral antigen 2B (red). Nuclear DNA is stained with Hoechst 33342 (blue). Arrows indicate areas protected upon mild permeabilization in cells incubated with choline-supplemented medium. B. Visualization of dsRNA in HeLa cells processed and infected as in A after Triton X100 permeabilization. Red arrows indicate dsRNA association with the nuclear envelope (PN) in choline-deprived cells; white arrows show big perinuclear blobs (CYT) of dsRNA signal reflecting normal development of replication membranes in choline-supplemented cells. C. HeLa cells were infected with poliovirus at an MOI of 10 PFU/cell after choline deprivation and incubated in a choline-free or a choline-supplemented medium for 4 h p.i. The cells were permeabilized with digitonin and treated (lines 3 and 4) or non-treated (lines 1 and 2) with proteinase K. * indicates protein fragments generated upon proteinase K treatment. Actin is shown as a loading control.