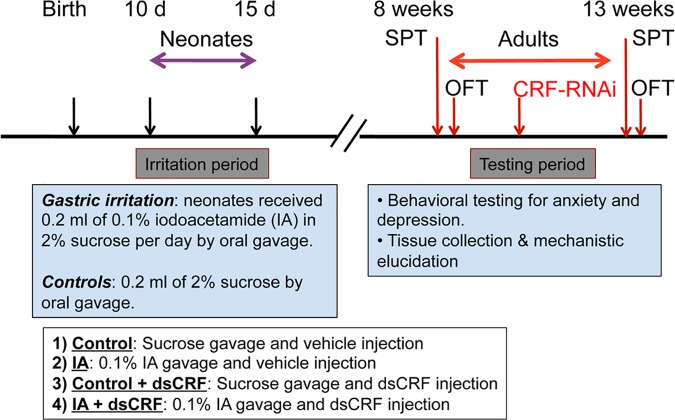
Fig 1. Schematic representation of FD model with time line for IA treatment, CRF-RNAi surgeries, and behavioral testing.
To induce FD, ten-day old rat pups received IA or sucrose (control) by gavage. Eight weeks later, baseline behavioral tests (SPT and OFT) were conducted. Surgery for gastric RNAi injection (RNAi against CRF or vehicle control) was performed 1 week after behavioral testing and 5 days after surgery, behavioral tests (SPT and OFT) were repeated. Thus, the same rats served as their own baseline for behavioral testing. One week after surgery, rats were euthanized and various tissue samples harvested and blood collected. At 10-day of age, male rat pups were randomized to either control (2% sucrose gavage) or FD (0.1% IA gavage) groups (n = 16/group). At 8 weeks after gastric irritation, adult rats in control and FD groups were then randomized to receive the following surgical treatments: Group 1 (Control): Sucrose + vehicle injection (n = 8), Group 2 (IA): IA + vehicle injection (n = 8), Group 3 (Control dsCRF): Sucrose + dsCRF injection (n = 8), and Group 4 (IA dsCRF): IA + dsCRF injection (n = 8).