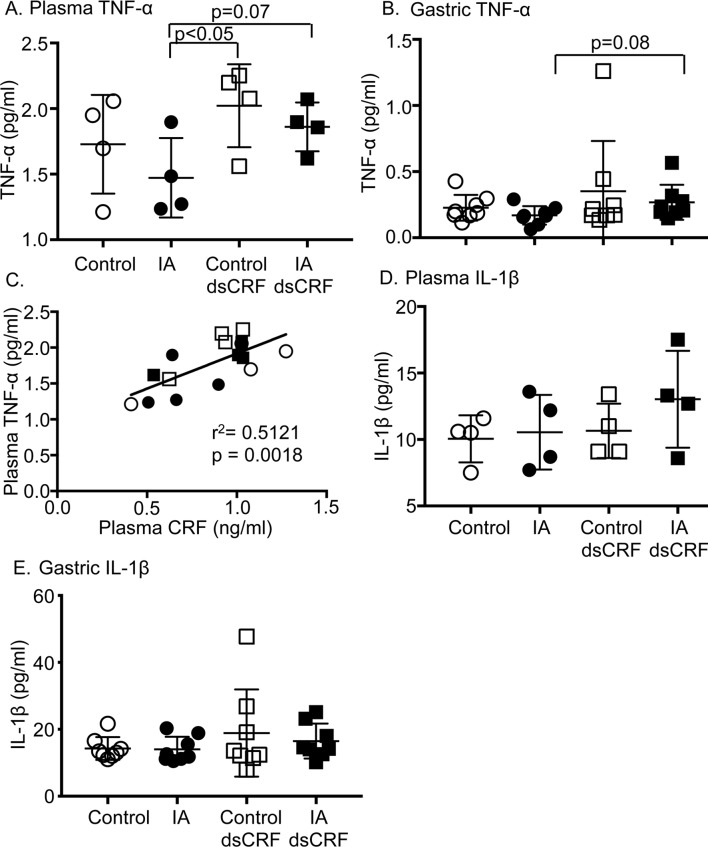
Fig 7. Modulation of cytokine levels in FD.
(A) Two-way ANOVA indicates significant main effect of CRF-RNAi on plasma TNF-α levels (p<0.05). Plasma TNF-α levels increased after CRF-RNAi treatment (p = 0.07; Student’s t-test; IA: 1.47 ± 0.15 vs. IA dsCRF: 1.86 ± 0.09; n = 4/group and p< 0.05; Student’s t-test; IA: 1.47 ± 0.15 vs. Control dsCRF: 2.02 ± 0.16; n = 4/group). (B) Gastric TNF-α levels tended to increase after CRF-RNAi in IA rats (p = 0.08; Student’s t-test; IA dsCRF: 0.27 ± 0.04 vs. IA: 0.17 ± 0.02; n = 8/group). (C) Linear regression analyses showed that plasma TNF-α levels were directly proportional to plasma CRF levels. Empty circles (Control), filled circles (IA), empty squares (Control dsCRF), and filled squares (IA dsCRF). (D) Plasma IL-1β levels (n = 4/group) and (E) gastric IL-1β showed no significant differences between the 4 groups (n = 8/group).