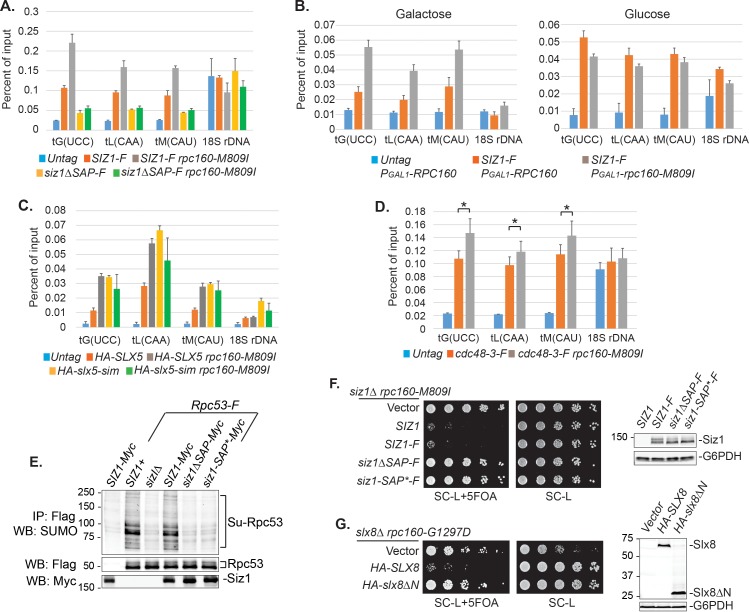
Figure 7. DNA is involved in Pol III repression.
(A) Chromatin IP of Siz1-Flag. An untagged strain was used as negative control. Chromatin association was determined by real-time PCR of the indicated genomic loci, using the percent of input method. Data are mean ± standard deviation calculated from six data points (two biological replicates and three technical replicates). (B) Plasmids carrying GAL1 promoter-driven RPC160 or rpc160-M809I were transformed in untagged or Flag-tagged SIZ1 cells as indicated. Cells were grown in galactose (left) or glucose (right) media to activate or inhibit transcription from the GAL1 promoter, respectively, followed by ChIP analysis of Siz1-Flag. All strains also express wild-type RPC160 from its endogenous promoter. (C–D) Similar ChIP analysis of HA-Slx5 and Cdc48-3-Flag as in (A). * p-value<0.05. (E) Flag-tagged Rpc53 proteins were purified from the indicated wild type or siz1 mutant strains, using anti-Flag beads, followed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using an anti-SUMO antibody. Rpc53 was detected by an anti-Flag antibody, and Siz1 was detected by an anti-Myc antibody. Either truncation (ΔSAP) or point mutation (SAP*) of the SAP domain resulted in loss of Rpc53 sumoylation. (F) Left: LEU2 plasmids carrying wild type or mutant SIZ1 alleles were transformed into an rpc160-M809I siz1Δ strain containing a URA3 RPC160 plasmid. Transformants were selected on SC-L plate, then spotted in fivefold dilution onto a SC-L + 5 FOA plate. Wild type SIZ1 complemented siz1Δ so the cells became sick on SC-L + 5 FOA plate, while the SAP mutants did not complement. Right: Comparable amounts of wild type and mutant Siz1 proteins were determined by anti-Flag immunoblotting on whole cell lysate, using G6PDH as loading control. (G) Similar plasmid shuffle experiment as in (F). LEU2 plasmids carrying HA-tagged wild-type SLX8 or slx8ΔN (Δ2–163) were transformed into an rpc160-G1297D slx8Δ strain containing a URA3 RPC160 plasmid. Wild-type SLX8 complemented slx8Δ, while slx8ΔN did not. Comparable amounts of Slx8 proteins were determined by an anti-HA immunoblot.