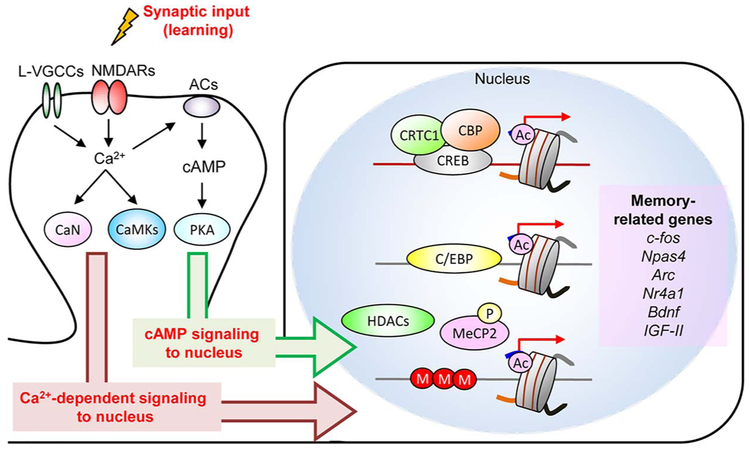
Fig. 1.
Learning-dependent gene expression program required for memory formation.
Activation of L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channel (L-VGCCs) and NMDA receptors (NMDARs) triggers calcium influx and induce calcium-dependent signaling molecules such as calcineurin (CaN) and Ca2+/cal-modulin-dependent protein kinases (CaMKs). Calcium influx also activates cAMP signaling pathway such as protein kinase (PKA) via Ca2+-sensitive adenylate cyclase (ACs). These molecules regulate the activity of transcription modulators (CREB, CBP, HDACs, CRTC1, and MeCP2) via phosphorylation and dephosphorylation. These transcriptional modulators contribute to the control of activity-dependent gene transcription which is required for synaptic plasticity and memory formation. Ac: acetylation: P: phosphorylation; M: DNA methylation.