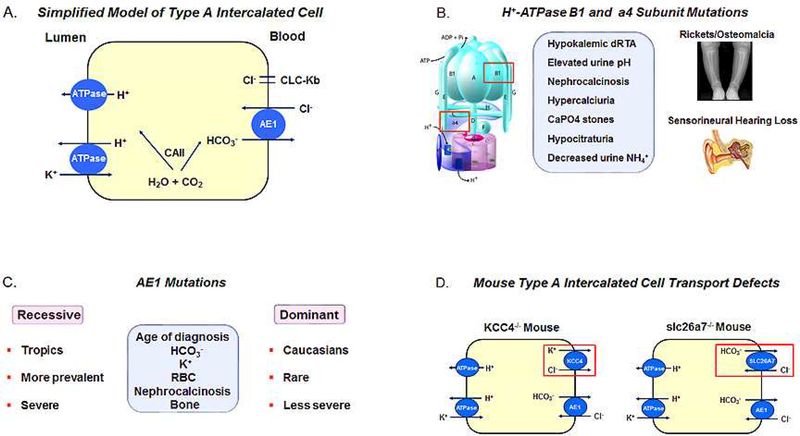
Figure 3.
(A) Type A intercalated cell H+/base transport processes; (B) Patients with H+-ATPase B1 or a4 mutations have Type I RTA with sensorineural deficits, hypokalemia, hypercalciuria, nephrocalcinosis and renal calculi. Bone abnormalities i.e. rickets versus osteomalacia are age dependent; (C) AE1 mutations are more commonly inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern with a greater frequency in the tropics. Autosomal dominant disease is less common and less severe than patients with recessive mutations, and typically is diagnosed in Caucasians. Patients lack sensorineural hearing abnormalities and the phenotype in general is otherwise similar to patients with H+-ATPase subunit mutations; (D) Loss of KCC4 and slc26a7 in the mouse Type A IC cause distal acidification defects. Mutations in these transporters in humans have not been documented.